,
observations: { guardianAddr: string; signature: string }[],
currentGuardians: string[],
guardianSetIndex: number
) {
console.log('Replacing Signatures...');
try {
if (!vaa) throw new Error('VAA is undefined or empty.');
if (currentGuardians.length === 0)
throw new Error('Guardian set is empty.');
if (observations.length === 0) throw new Error('No observations provided.');
const validSigs = observations.filter((sig) =>
currentGuardians.includes(sig.guardianAddr)
);
if (validSigs.length === 0)
throw new Error('No valid signatures found. Cannot proceed.');
const formattedSigs = validSigs
.map((sig) => {
try {
const sigBuffer = Buffer.from(sig.signature, 'base64');
// If it's 130 bytes, it's hex-encoded and needs conversion
const sigBuffer1 =
sigBuffer.length === 130
? Buffer.from(sigBuffer.toString(), 'hex')
: sigBuffer;
const r = BigInt('0x' + sigBuffer1.subarray(0, 32).toString('hex'));
const s = BigInt('0x' + sigBuffer1.subarray(32, 64).toString('hex'));
const vRaw = sigBuffer1[64];
const v = vRaw < 27 ? vRaw : vRaw - 27;
return {
guardianIndex: currentGuardians.indexOf(sig.guardianAddr),
signature: new Signature(r, s, v),
};
} catch (error) {
console.error(
`Failed to process signature for guardian: ${sig.guardianAddr}`,
error
);
return null;
}
})
.filter(
(sig): sig is { guardianIndex: number; signature: Signature } =>
sig !== null
); // Remove null values
let parsedVaa: VAA<'Uint8Array'>;
try {
parsedVaa = deserialize('Uint8Array', vaa);
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Error deserializing VAA: ${error}`);
}
const outdatedGuardianIndexes = parsedVaa.signatures
.filter(
(vaaSig) =>
!formattedSigs.some(
(sig) => sig.guardianIndex === vaaSig.guardianIndex
)
)
.map((sig) => sig.guardianIndex);
console.log('Outdated Guardian Indexes:', outdatedGuardianIndexes);
let updatedSignatures = parsedVaa.signatures.filter(
(sig) => !outdatedGuardianIndexes.includes(sig.guardianIndex)
);
const validReplacements = formattedSigs.filter(
(sig) =>
!updatedSignatures.some((s) => s.guardianIndex === sig.guardianIndex)
);
// Check if we have enough valid signatures to replace outdated ones**
if (outdatedGuardianIndexes.length > validReplacements.length) {
console.warn(
`Not enough valid replacement signatures! Need ${outdatedGuardianIndexes.length}, but only ${validReplacements.length} available.`
);
return;
}
updatedSignatures = [
...updatedSignatures,
...validReplacements.slice(0, outdatedGuardianIndexes.length),
];
updatedSignatures.sort((a, b) => a.guardianIndex - b.guardianIndex);
const updatedVaa: VAA<'Uint8Array'> = {
...parsedVaa,
guardianSet: guardianSetIndex,
signatures: updatedSignatures,
};
let patchedVaa: Uint8Array;
try {
patchedVaa = serialize(updatedVaa);
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Error serializing updated VAA: ${error}`);
}
try {
if (!(patchedVaa instanceof Uint8Array))
throw new Error('Patched VAA is not a Uint8Array!');
const vaaHex = `0x${Buffer.from(patchedVaa).toString('hex')}`;
console.log('Sending updated VAA to RPC...');
const result = await axios.post(RPC, {
jsonrpc: '2.0',
id: 1,
method: 'eth_call',
params: [
{
from: null,
to: ETH_CORE,
data: eth.abi.encodeFunctionCall(PARSE_AND_VERIFY_VM_ABI, [vaaHex]),
},
'latest',
],
});
const verificationResult = result.data.result;
console.log('Updated VAA (hex):', vaaHex);
return verificationResult;
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Error sending updated VAA to RPC: ${error}`);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Unexpected error in replaceSignatures:', error);
}
}
```
## Create Script to Replace Outdated VAA Signatures
Now that we have all the necessary helper functions, we will create a script to automate replacing outdated VAA signatures. This script will retrieve a transaction’s VAA sequentially, check its validity, fetch the latest Guardian set, and update its signatures. By the end, it will output a correctly signed VAA that can be proposed for Guardian approval.
1. **Open the file**: Inside `src/scripts/replaceSignatures.ts`, import the required helper functions needed to process the VAAs.
```typescript title="src/scripts/replaceSignatures.ts"
fetchVaaId,
fetchVaa,
checkVaaValidity,
fetchObservations,
fetchGuardianSet,
replaceSignatures,
} from '../helpers/vaaHelper';
import { TXS } from '../config/constants';
```
2. **Define the main execution function**: Add the following function inside `src/scripts/replaceSignatures.ts` to process each transaction in `TXS`, going step by step through the signature replacement process.
```typescript
try {
for (const tx of TXS) {
console.log(`\nProcessing TX: ${tx}\n`);
// 1. Fetch Transaction VAA IDs:
const vaaIds = await fetchVaaId([tx]);
if (!vaaIds.length) continue;
// 2. Fetch VAA Data:
const vaaData = await fetchVaa(vaaIds);
if (!vaaData.length) continue;
const vaaBytes = vaaData[0].vaaBytes;
if (!vaaBytes) continue;
// 3. Check VAA Validity:
const { valid } = await checkVaaValidity(vaaBytes);
if (valid) continue;
// 4. Fetch Observations (VAA signatures):
const observations = await fetchObservations(vaaIds[0]);
// 5. Fetch Current Guardian Set:
const [currentGuardians, guardianSetIndex] = await fetchGuardianSet();
// 6. Replace Signatures:
const response = await replaceSignatures(
Buffer.from(vaaBytes, 'base64'),
observations,
currentGuardians,
guardianSetIndex
);
if (!response) continue;
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('❌ Error in execution:', error);
process.exit(1);
}
}
```
3. **Make the script executable**: Ensure it runs when executed.
```typescript
```
To run the script, use the following command:
```bash
npx tsx src/scripts/replaceSignatures.ts
```
npx tsx src/scripts/replaceSignatures.ts
Processing TX: 0x3ad91ec530187bb2ce3b394d587878cd1e9e037a97e51fbc34af89b2e0719367
❌ VAA Valid: false, Reason: VM signature invalid
Fetching observations
Fetching current guardian set
Replacing Signatures...
Outdated Guardian Indexes: [ 0 ]
Sending updated VAA to RPC...
Updated VAA (hex): 0x01000000040d010019447b72d51e33923a3d6b28496ccd3722d5f1e33e2...
The script logs each step, skipping valid VAAs, replacing outdated signatures for invalid VAAs, and logging any errors. It then completes with a valid VAA ready for submission.
## Resources
You can explore the complete project and find all necessary scripts and configurations in Wormhole's [demo GitHub repository](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/demo-vaa-signature-replacement){target=\_blank}.
The demo repository includes a bonus script to check the VAA redemption status on Ethereum and Solana, allowing you to verify whether a transaction has already been redeemed on the destination chain.
## Conclusion
You've successfully built a script to fetch, validate, and replace outdated signatures in VAAs using Wormholescan and the Wormhole SDK.
It's important to note that this tutorial does not update VAAs in the Wormhole network. Before redeeming the VAA, you must propose it for Guardian approval to finalize the process.
Looking for more? Check out the [Wormhole Tutorial Demo repository](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/demo-tutorials){target=\_blank} for additional examples.
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/architecture.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Architecture
description: Overview of Wormhole's architecture, detailing key on-chain and off-chain components like the Core Contract, Guardian Network, and relayers.
categories: Basics
---
# Architecture
Wormhole has several noteworthy components. Before discussing each component in depth, this page will provide an overview of how the major pieces fit together.
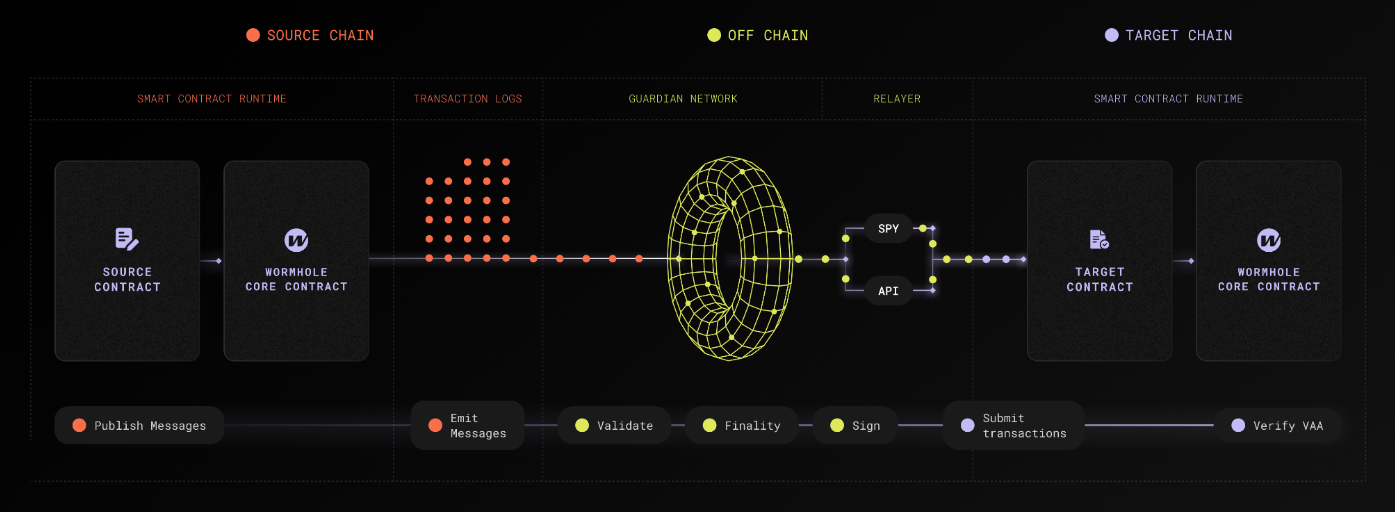
The preceding diagram outlines the end-to-end flow of multichain communication through Wormhole's architecture, which is described as follows:
1. **Source chain**: A source contract emits a message by interacting with the [Wormhole Core Contract](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/core-contracts/){target=\_blank} on the source chain, which publishes the message in the blockchain's transaction logs.
2. **Guardian Network**: [Guardians](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/guardians/){target=\_blank} validate these messages and sign them to produce [Verifiable Action Approvals (VAAs)](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas/){target=\_blank}.
3. **Relayers**: Off-chain relayers or applications fetch the VAA and relay it to the target chain.
4. **Target chain**: On the target chain, the message is consumed by the appropriate contract. This contract interacts with the Wormhole Core Contract to verify the VAA and execute the intended multichain operation.
The flow from the relayer to the target chain involves an entry point contract, which could vary based on the use case:
- In some applications, the target contract acts as the entry point and performs verification via the Core Contract.
- In products like Wrapped Token Transfers (WTT), the WTT contract itself interacts with the Core Contract.
## On-Chain Components
- **Emitter**: A contract that calls the publish message method on the Core Contract. To identify the message, the Core Contract will write an event to the transaction logs with details about the emitter and sequence number. This may be your cross-chain dApp or an existing ecosystem protocol.
- **[Wormhole Core Contract](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/core-contracts/){target=\_blank}**: Primary contract, this is the contract which the Guardians observe and which fundamentally allows for multichain communication.
- **Transaction logs**: Blockchain-specific logs that allow the Guardians to observe messages emitted by the Core Contract.
## Off-Chain Components
- **Guardian Network**: Validators that exist in their own P2P network. Guardians observe and validate the messages emitted by the Core Contract on each supported chain to produce VAAs (signed messages).
- **[Guardian](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/guardians/){target=\_blank}**: One of 19 validators in the Guardian Network that contributes to the VAA multisig.
- **[Spy](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/spy/){target=\_blank}**: A daemon that subscribes to messages published within the Guardian Network. A Spy can observe and forward network traffic, which helps scale up VAA distribution.
- **[API](https://docs.wormholescan.io/){target=\_blank}**: A REST server to retrieve details for a VAA or the Guardian Network.
- **[VAAs](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas/){target=\_blank}**: Verifiable Action Approvals (VAAs) are the signed attestation of an observed message from the Wormhole Core Contract.
- **[Relayer](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/relayer/){target=\_blank}**: Any off-chain process that relays a VAA to the target chain.
- **Wormhole relayers**: A decentralized relayer network that delivers messages that are requested on-chain via the Wormhole relayer contract.
- **Custom relayers**: Relayers that only handle VAAs for a specific protocol or multichain application. They can execute custom logic off-chain, reducing gas costs and increasing multichain compatibility. Currently, multichain application developers are responsible for developing and hosting custom relayers.
## Next Steps
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Core Contracts**
---
Discover Wormhole's Core Contracts, enabling multichain communication with message sending, receiving, and multicast features for efficient synchronization.
[:custom-arrow: Explore Core Contracts](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/core-contracts/)
- :octicons-tools-16:{ .lg .middle } **Core Messaging**
---
Follow the guides in this section to work directly with the building blocks of Wormhole messaging, Wormhole-deployed relayers and Core Contracts, to send, receive, validate, and track multichain messages.
[:custom-arrow: Build with Core Messaging](/docs/products/messaging/guides/wormhole-relayers/)
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/ecosystem.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Ecosystem
description: Explore Wormhole's modular ecosystem of cross-chain tools for messaging, bridging, governance, and developer integration.
categories: Basics
---
# The Wormhole Ecosystem
[Wormhole](/docs/protocol/introduction/){target=\_blank} is a cross-chain messaging protocol connecting decentralized applications across multiple blockchains. It offers a suite of interoperability tools, each addressing different multichain challenges, and allows developers to mix and match these products as needed.
Whether you’re looking for a simple UI-based bridging experience, a native token transfer flow without wrapped assets, real-time cross-chain data queries, or an advanced settlement layer for complex asset movements, Wormhole has a product designed for that purpose. Every solution integrates with Wormhole’s core messaging network, ensuring each module can operate independently or in combination with others.
This page will guide you through the structural layout of these tools—how they fit together, can be used independently, and can be layered to build robust, multichain applications.
## Ecosystem Overview
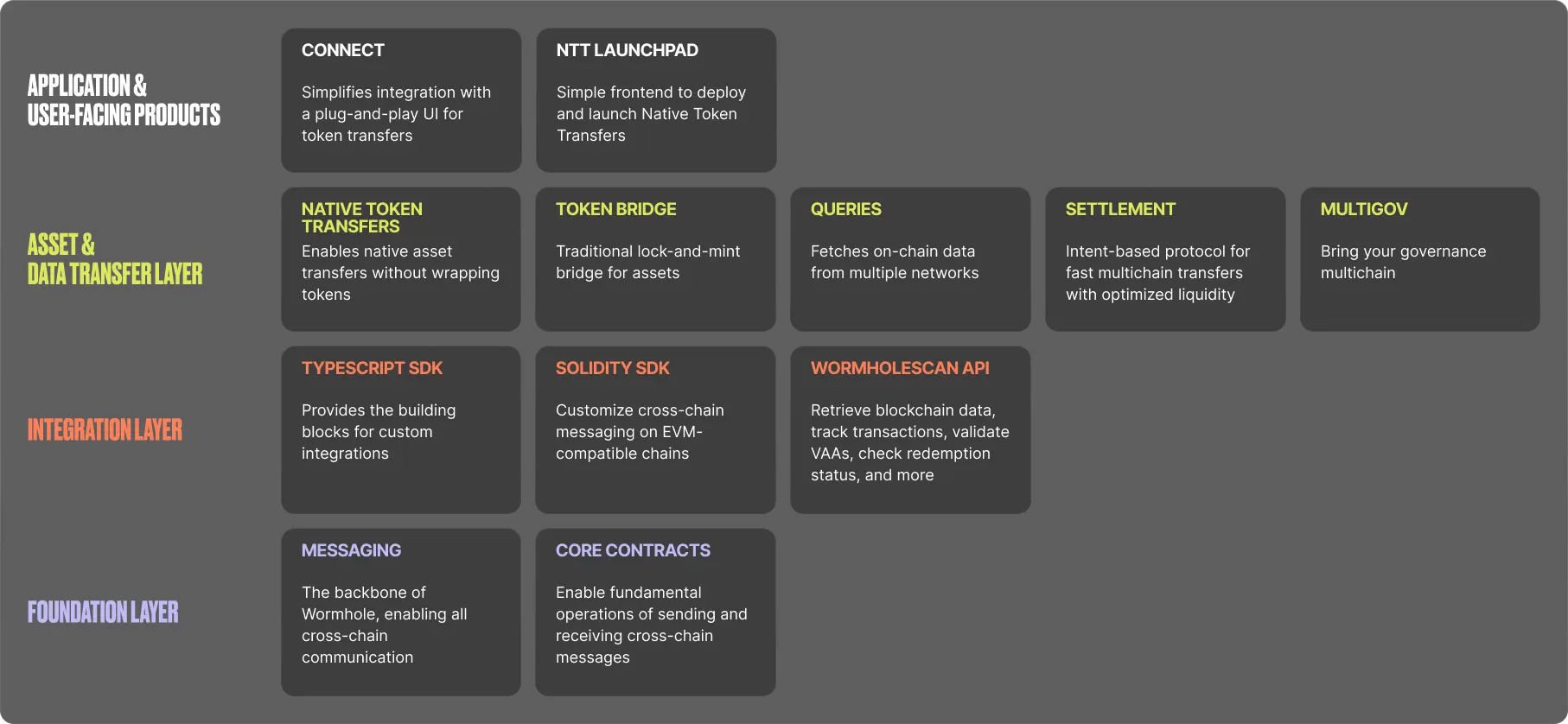
The diagram shows a high-level view of Wormhole’s modular stack, illustrating how different tools are grouped into four layers:
- **Application and user-facing products**: The top layer includes user-centric solutions such as [Connect](/docs/products/connect/overview/){target=\_blank} (a simple bridging interface).
- **Asset and data transfer layer**: Below it sits the core bridging and data solutions—[NTT](/docs/products/token-transfers/native-token-transfers/overview/){target=\_blank}, [WTT](/docs/products/token-transfers/wrapped-token-transfers/overview/){target=\_blank}, [Queries](/docs/products/queries/overview/){target=\_blank}, [Settlement](/docs/products/settlement/overview/){target=\_blank}, and [MultiGov](/docs/products/multigov/overview/){target=\_blank}—that handle the movement of tokens, real-time data fetching, advanced cross-chain settlements, and cross-chain governance.
- **Integration layer**: The [TypeScript SDK](/docs/tools/typescript-sdk/get-started/){target=\_blank} and [WormholeScan API](https://wormholescan.io/#/){target=\_blank} provide developer-friendly libraries and APIs to integrate cross-chain capabilities into applications.
- **Foundation layer**: At the base, the [Wormhole messaging](/docs/products/messaging/overview/){target=\_blank} system and the [core contracts](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/core-contracts/){target=\_blank} secure the entire network, providing essential verification and cross-chain message delivery.
## Bringing It All Together: Interoperability in Action
Wormhole’s modularity makes it easy to adopt just the pieces you need. If you want to quickly add bridging to a dApp, use Connect at the top layer while relying on the Foundation Layer behind the scenes. Or if your app needs to send raw messages between chains, integrate the Messaging layer directly via the Integration Layer (TypeScript or Solidity SDK). You can even layer on additional features—like real-time data calls from Queries or more flexible bridging flows with Native Token Transfers.
Ultimately, these components aren’t siloed but designed to be combined. You could, for instance, fetch a balance from one chain using Queries and then perform an on-chain swap on another chain using Settlement. Regardless of your approach, each Wormhole product is powered by the same Guardian-secured messaging backbone, ensuring all cross-chain interactions remain reliable and secure.
## Next Steps
Unsure which bridging solution you need? Visit the [Product Comparison](/docs/products/overview/){target=\_blank} page to quickly match your requirements with the right Wormhole tool.
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/infrastructure/core-contracts.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Core Contracts
description: Discover Wormhole's Core Contracts, which enable multichain communication with message sending, receiving, and multicast features for efficient synchronization.
categories: Basics
---
# Core Contracts
The Wormhole Core Contract is deployed across each supported blockchain network. This contract is a fundamental component of the Wormhole interoperability protocol and acts as the foundational layer enabling secure and efficient multichain messaging. All multichain applications either interact directly with the Core Contract or with another contract that does.
This page summarizes the key functions of the Core Contract and outlines how the Core Contract works.
## Key Functions
Key functions of the Wormhole Core Contract include the following:
- **Multichain messaging**: Standardizes and secures the format of messages to facilitate consistent communication for message transfer between Wormhole-connected blockchain networks, allowing developers to leverage the unique features of each network.
- **Verification and validation**: Verifies and validates all VAAs received on the target chain by confirming the Guardian signature to ensure the message is legitimate and has not been manipulated or altered.
- **Guardian Network coordination**: Coordinates with Wormhole's Guardian Network to facilitate secure, trustless communication across chains and ensure that only validated interactions are processed to enhance the protocol's overall security and reliability.
- **Event emission for monitoring**: Emits events for every multichain message processed, allowing for network activity monitoring like tracking message statuses, debugging, and applications that can react to multichain events in real time.
## How the Core Contract Works
The Wormhole Core Contract is central in facilitating secure and efficient multichain transactions. It enables communication between different blockchain networks by packaging transaction data into standardized messages, verifying their authenticity, and ensuring they are executed correctly on the destination chain.
The following describes the role of the Wormhole Core Contract in message transfers:
1. **Message submission**: When a user initiates a multichain transaction, the Wormhole Core Contract on the source chain packages the transaction data into a standardized message payload and submits it to the Guardian Network for verification.
2. **Guardian verification**: The Guardians independently observe and sign the message. Once enough Guardians have signed the message, the collection of signatures is combined with the message and metadata to produce a VAA.
3. **Message reception and execution**: On the target chain, the Wormhole Core Contract receives the verified message, checks the Guardians' signatures, and executes the corresponding actions like minting tokens, updating states, or calling specific smart contract functions.
For a closer look at how messages flow between chains and all of the components involved, you can refer to the [Architecture Overview](/docs/protocol/architecture/) page.
### Message Submission
You can send multichain messages by calling a function against the source chain Core Contract, which then publishes the message. Message publishing strategies can differ by chain; however, generally, the Core Contract posts the following items to the blockchain logs:
- **`emitterAddress`**: The contract which made the call to publish the message.
- **`sequenceNumber`**: A unique number that increments for every message for a given emitter (and implicitly chain).
- **`consistencyLevel`**: The level of finality to reach before the Guardians will observe and attest the emitted event. This is a defense against reorgs and rollbacks since a transaction, once considered "final," is guaranteed not to have the state changes it caused rolled back. Since different chains use different consensus mechanisms, each one has different finality assumptions, so this value is treated differently on a chain-by-chain basis. See the options for finality for each chain in the [Wormhole Finality](/docs/products/reference/consistency-levels/){target=\_blank} reference page.
There are no fees to publish a message except when publishing on Solana, but this is subject to change in the future.
### Message Reception
When you receive a multichain message on the target chain Core Contract, you generally must parse and verify the [components of a VAA](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas#vaa-format){target=\_blank}. Receiving and verifying a VAA ensures that the Guardian Network properly attests to the message and maintains the integrity and authenticity of the data transmitted between chains.
## Multicast
Multicast refers to simultaneously broadcasting a single message or transaction across different blockchains with no destination address or chain for the sending and receiving functions. VAAs attest that "this contract on this chain said this thing." Therefore, VAAs are multicast by default and will be verified as authentic on any chain where they are used.
This multicast-by-default model makes it easy to synchronize state across the entire ecosystem. A blockchain can make its data available to every chain in a single action with low latency, which reduces the complexity of the n^2 problems encountered by routing data to many blockchains.
This doesn't mean an application _cannot_ specify a destination address or chain. For example, the [Wrapped Token Transfers (WTT)](/docs/products/token-transfers/wrapped-token-transfers/overview/){target=\_blank} and [Wormhole relayer](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/relayer/){target=\_blank} contracts require that some destination details be passed and verified on the destination chain.
Because the VAA creation is separate from relaying, the multicast model does not incur an additional cost when a single chain is targeted. If the data isn't needed on a certain blockchain, don't relay it there, and it won't cost anything.
## Next Steps
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Verified Action Approvals (VAA)**
---
Learn about Verified Action Approvals (VAAs) in Wormhole, their structure, validation, and their role in multichain communication.
[:custom-arrow: Learn About VAAs](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas/)
- :octicons-tools-16:{ .lg .middle } **Get Started with Core Contracts**
---
This guide walks through the key methods of the Core Contracts, providing you with the knowledge needed to integrate them into your multichain contracts.
[:custom-arrow: Build with Core Contracts](/docs/products/messaging/guides/core-contracts/)
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/infrastructure/guardians.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Guardians
description: Explore Wormhole's Guardian Network, a decentralized system for secure, scalable cross-chain communication across various blockchain ecosystems.
categories: Basics
---
# Guardians
Wormhole relies on a set of 19 distributed nodes that monitor the state on several blockchains. In Wormhole, these nodes are referred to as Guardians. The current Guardian set can be seen in the [Dashboard](https://wormhole-foundation.github.io/wormhole-dashboard/#/?endpoint=Mainnet){target=\_blank}.
Guardians fulfill their role in the messaging protocol as follows:
1. Each Guardian observes messages and signs the corresponding payloads in isolation from the other Guardians.
2. Guardians combine their independent signatures to form a multisig.
3. This multisig represents proof that a majority of the Wormhole network has observed and agreed upon a state.
Wormhole refers to these multisigs as [Verifiable Action Approvals](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas/){target=\_blank} (VAAs).
## Guardian Network
The Guardian Network functions as Wormhole's decentralized oracle, ensuring secure, cross-chain interoperability. Learning about this critical element of the Wormhole ecosystem will help you better understand the protocol.
The Guardian Network is designed to help Wormhole deliver on five key principles:
- **Decentralization**: Control of the network is distributed across many parties.
- **Modularity**: Independent components (e.g., oracle, relayer, applications) ensure flexibility and upgradeability.
- **Chain agnosticism**: Supports EVM, Solana, and other blockchains without relying on a single network.
- **Scalability**: Can handle large transaction volumes and high-value transfers.
- **Upgradeable**: Can change the implementation of its existing modules without breaking integrators to adapt to changes in decentralized computing.
The following sections explore each principle in detail.
### Decentralization
Decentralization remains the core concern for interoperability protocols. Earlier solutions were fully centralized, and even newer models often rely on a single entity or just one or two actors, creating low thresholds for collusion or failure.
Two common approaches to decentralization have notable limitations:
- **Proof-of-Stake (PoS)**: While PoS is often seen as a go-to model for decentralization, it's not well-suited for a network that verifies many blockchains and doesn't run its own smart contracts. Its security in this context is unproven, and it introduces complexities that make other design goals harder to achieve.
- **Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)**: ZKPs offer a trustless and decentralized approach, but the technology is still early-stage. On-chain verification is often too computationally expensive—especially on less capable chains—so a multisig-based fallback is still required for practical deployment.
In the current De-Fi landscape, most major blockchains are secured by a small group of validator companies. Only a limited number of companies worldwide have the expertise and capital to run high-performance validators.
If a protocol could unite many of these top validator companies into a purpose-built consensus mechanism designed for interoperability, it would likely offer better performance and security than a token-incentivized network. The key question is: how many of them could Wormhole realistically involve?
To answer that, consider these key constraints and design decisions:
- **Threshold signatures allow flexibility, but**: With threshold signatures, in theory, any number of validators could participate. However, threshold signatures are not yet widely supported across blockchains. Verifying them is expensive and complex, especially in a chain-agnostic system.
- **t-Schnorr multisig is more practical**: Wormhole uses [t-Schnorr multisig](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schnorr_signature){target=\_blank}, which is broadly supported and relatively inexpensive to verify. However, verification costs scale linearly with the number of signers, so the size of the validator set needs to be carefully chosen.
- **19 validators is the optimal tradeoff**: A set of 19 participants presents a practical compromise between decentralization and efficiency. With a two-thirds consensus threshold, only 13 signatures must be verified on-chain—keeping gas costs reasonable while ensuring strong security.
- **Security through reputation, not tokens**: Wormhole relies on a network of established validator companies instead of token-based incentives. These 19 Guardians are among the most trusted operators in the industry—real entities with a track record, not anonymous participants.
This forms the foundation for a purpose-built Proof-of-Authority (PoA) consensus model, where each Guardian has an equal stake. As threshold signatures gain broader support, the set can expand. Once ZKPs become widely viable, the network can evolve into a fully trustless system.
### Modularity
Wormhole is designed with simple components that are very good at a single function. Separating security and consensus (Guardians) from message delivery ([relayers](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/relayer/){target=\_blank}) allows for the flexibility to change or upgrade one component without disrupting the others.
### Chain Agnosticism
Today, Wormhole supports a broader range of ecosystems than any other interoperability protocol because it uses simple tech (t-schnorr signatures), an adaptable, heterogeneous relayer model, and a robust validator network. Wormhole can expand to new ecosystems as quickly as a [Core Contract](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/core-contracts/){target=\_blank} can be developed for the smart contract runtime.
### Scalability
Wormhole scales well, as demonstrated by its ability to handle substantial total value locked (TVL) and transaction volume even during tumultuous events.
Every Guardian must run a full node for every blockchain in the ecosystem. This requirement can be computationally heavy to set up; however, once all the full nodes are running, the Guardian Network's actual computation needs become lightweight.
Performance is generally limited by the speed of the underlying blockchains, not the Guardian Network itself.
### Upgradeable
Wormhole is designed to adapt and evolve in the following ways:
- **Guardian Set expansion**: Future updates may introduce threshold signatures to allow for more Guardians in the set.
- **ZKP integration**: As Zero-Knowledge Proofs become more widely supported, the network can transition to a fully trustless model.
These principles combine to create a clear pathway towards a fully trustless interoperability layer that spans decentralized computing.
## Next Steps
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Relayers**
---
Discover the role of relayers in the Wormhole network, including client-side, custom, and Wormhole-deployed types, for secure cross-chain communication.
[:custom-arrow: Learn About Relayers](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/relayer/)
- :octicons-tools-16:{ .lg .middle } **Query Guardian Data**
---
Learn how to use Wormhole Queries to add real-time access to Guardian-attested on-chain data via a REST endpoint to your dApp, enabling secure cross-chain interactions and verifications.
[:custom-arrow: Build with Queries](/docs/products/queries/overview/)
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/infrastructure/relayer.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Relayers
description: Discover the role of relayers in the Wormhole network, including client-side, custom, and Wormhole-deployed types, for secure cross-chain communication.
categories: Basics
---
# Relayers
This page provides a comprehensive guide to relayers within the Wormhole network, describing their role, types, and benefits in facilitating multichain processes.
Relaying refers to the process of delivering a cross-chain message, specifically a [Verified Action Approval (VAA)](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas/){target=\_blank}, from its source chain to the destination chain. In a multichain application, after a message is emitted on the source chain and signed by Wormhole’s Guardians, it must be carried over to the target chain’s contract – this is the relayer's responsibility.
Relayers do not need to be trusted; the security of Wormhole messages stems from the Guardian Network signatures on the VAA, which cannot be tampered with by relayers. In other words, a relayer cannot alter the content or outcome of a message – it can only affect when the message gets delivered (availability). This trust-minimized design means developers and users don’t have to trust a relayer service to preserve integrity, only to be online to forward the message.
## Fundamentals
This section highlights the crucial principles underpinning the operation and handling of relayers within the Wormhole network.
Relayers are fundamentally trustless entities within the network, meaning while they don't require your trust to operate, you also shouldn't trust them implicitly. They function as delivery mechanisms, transporting VAAs from their source to their destination.
- **Anyone can relay a message**: Guardians broadcast signed VAAs publicly, so any entity can retrieve a VAA and submit it to the destination chain’s contracts. The signatures provide universal verifiability; any Wormhole contract or client can check the Guardian signatures. These properties ensure that relaying can be permissionless and trustless. If one relayer is down, any other party (even the user) could take the VAA and deliver it. No relayer can forge or modify the message without invalidating the signatures.
- **Security is in the VAA**: The Wormhole Guardians’ signatures authenticate the message. A relayer might provide additional info or off-chain data, but contracts should not rely on anything that isn’t from a verified VAA or on-chain source. This ensures that even though relayers operate off-chain, they cannot compromise the application’s logic or funds. In summary, Wormhole relayers can’t compromise security, only availability – if a relayer misbehaves, the worst outcome is a delayed or missed delivery, not a falsified message.
- **User experience vs. infrastructure**: Relayers exist to improve user experience by automating cross-chain steps that would otherwise be manual. However, using relayers introduces considerations around fees and infrastructure. Developers must either rely on an external relayer service or run their own. Wormhole’s design offers flexibility: developers can choose an entirely client-side (no relayer) approach or opt for either Wormhole-provided relayer networks or custom relayers that developers build themselves. Each approach has its benefits and trade-offs in terms of complexity, cost, and control, as we explore next.
## Manual vs. Automated Relaying
When integrating Wormhole messaging, developers must choose between manual (client-side) relaying and automated relaying. The distinction lies in the entity responsible for delivering the VAA to the target chain.
- **Manual relaying (client-side)**: This approach puts the burden on the user or their client (e.g., a dApp or wallet) to carry out all cross-chain steps. After an action on chain A produces a VAA, the user must manually fetch that VAA (typically via a Wormhole API or explorer) and then submit it in a transaction on chain B. No specialized backend is needed. The relayer role is handled directly by the user via their wallet or web browser. The advantage lies in the simplicity of architecture (no extra services to run) and no additional fees beyond the target chain’s transaction fees. However, this approach provides a limited user experience beyond basic demos, as it requires users to sign multiple transactions and maintain funds on each chain involved. This process can be cumbersome and error-prone, as the additional step may be unclear and lead to drop-offs. In summary, manual relaying is suitable for testing and MVPs, but it's not ideal for production-grade applications.
- **Automated relaying**: In this approach, the cross-chain delivery is handled automatically by a relayer service or network, rather than the end-user. From the user’s perspective, the message is delivered to the target chain without requiring manual intervention. Automated relaying significantly improves the user experience by allowing an asset transfer to be initiated with a single action, after which the funds are delivered to the destination chain. There are two ways to achieve automated relaying:
- **Build a relayer service (custom backend)**: Run an off-chain service that listens for VAAs and forwards them. This approach provides full control (e.g., gas optimization, batch transactions, retry handling), but requires building and maintaining backend infrastructure.
- **Use a relayer network provided by Wormhole**: Leverage Wormhole’s decentralized relayer service, which requires minimal integration and no infrastructure to run. Developers can request delivery of messages through on-chain calls, while an untrusted external delivery provider handles execution. This removes the need to run a service, at the cost of service fees, and shifts the complexity away from the user, resulting in a smoother experience.
Choosing between manual and automated relaying often comes down to the specific needs of the product. If the integrator prioritizes convenience, automated relaying (via either a Wormhole service or a custom service) provides a superior experience.
| Aspect | Manual Relaying (Client-Side) | Automated Relaying |
|----------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------|
| VAA Delivery | User or client application | Relayer service or network (custom or Wormhole) |
| Infrastructure | None required | Either a backend service or Wormhole’s relayer network |
| User Experience | Multiple signatures, funds on each chain, extra manual step | One-click transfers, message delivered automatically |
| Cost Model | Only target chain transaction fees | Service fees + destination chain gas |
| Reliability | Depends on user completing all steps | Relayer handles retries and execution |
| Best Suited For | Testing, MVPs, demos | Production-grade applications prioritizing UX |
## Wormhole Relayers
To simplify the adoption of automated relaying, Wormhole provides its relayer infrastructure and APIs for developers to utilize. Wormhole Relayers is an umbrella term for Wormhole’s suite of relayer solutions, which currently includes the [messaging executor framework](#executor) and the [standard relayer](#standard-relayer) (currently being phased out), as well as the option of building [custom relayers](#custom-relaying) using Wormhole’s tooling. All of these approaches adhere to Wormhole’s core principle of trustless delivery – not trusting the Wormhole relayer operators any more than any blockchain infrastructure. Below is an overview of each option and its role in cross-chain dApp development.
Wormhole currently supports three types of relayers:
- **Executor**: A permissionless, next-generation framework that enables anyone to act as a relayer, with support for multichain delivery and custom pricing through a request–quote model.
- **Standard relayer**: A Wormhole-operated network available out of the box for EVM chains, providing simple integration without backend infrastructure.
- **Custom relayer**: An application-run service tailored to specific needs, offering maximum flexibility and optimization at the cost of higher operational overhead.
| Aspect | Executor. | Standard Relayer. | Custom Relayer. |
|-----------------|--------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------|------------------------------|
| Who Runs It | Permissionless network of providers | Wormhole contributor–run nodes | Application team |
| Chain Support | Multichain, including non-EVM | EVM only | Any Wormhole-supported chain |
| Integration | Executor contracts with request–quote model | On-chain functions | Custom backend service |
| Infrastructure | None (on-chain only) | None (on-chain only) | Full backend required, 24/7 availability |
| User Experience | Seamless, broader chain support | Seamless, EVM only | App-specific optimizations possible |
| Trade-offs | Early rollout, limited initial availability | EVM-only, no off-chain logic | High DevOps cost, must stay secure |
### Executor
The Executor is Wormhole’s next-generation cross-chain execution framework, designed to extend relaying functionality beyond EVM chains and add greater flexibility to how deliveries are processed. The Executor system enables anyone to act as a relayer (often referred to as an execution provider) in a permissionless network, introducing a request-and-quote model for delivering messages. The Executor architecture still relies on the core Wormhole guarantees (VAAs for security, Guardian verification), but it changes how the relaying service is accessed and who can fulfill it.
In the Executor model, Wormhole deploys a lightweight Executor Contract on every supported chain. This contract is stateless and permissionless, meaning it isn’t owned by any relayer, and anyone can interact with it. When an application wants to request a cross-chain message delivery via the Executor, it will call this contract on the source chain, providing the details of the target chain, target address, and a fee quote signed by a chosen executor provider. The Executor contract essentially records an Execution Request (and escrows the payment, including a small fee), which off-chain executor nodes are listening for (via events). An available executor node that corresponds to the provided quote will then take the VAA and execute the message on the destination chain, similar to how the standard relayer would — for example, calling the target contract with the message payload. Because the execution network is open, different providers can offer quotes (pricing) for delivering a message, and developers or users can choose competitively. This fosters a decentralized marketplace of relayers, rather than a single service.
```mermaid
sequenceDiagram
participant App as Application
participant ExContract as Executor Contract (Source Chain)
participant ExecNode as Executor Node (Off-chain)
participant Dest as Target Contract (Destination Chain)
App->>ExContract: Submit Execution Request
(target chain, target address, fee quote)
ExContract->>ExecNode: Emit event with request + escrowed fee
ExecNode-->>ExecNode: Listen for events
Match signed quote
ExecNode->>Dest: Deliver VAA + execute message payload
Dest-->>App: Target contract logic executed
```
For developers, integrating the Executor framework can be as straightforward as using the standard relayer, with the added benefit of supporting non-EVM chains and custom pricing logic. It’s described as _a permissionless, extensible, and low-overhead cross-chain execution framework_. The extensibility means the system is built to accommodate various message types and future features, and permissionless means integrators are not tied to a single provider – it is possible to run an executor node if desired, or rely on community-run services. The Executor is part of Wormhole’s effort to make relaying truly multichain. For example, delivering messages to Solana or other ecosystems where an EVM-style relayer contract is insufficient will be possible through this framework.
The Messaging Executor is a recent addition, and its availability might initially be limited to specific chains as it rolls out. It works alongside the Wormhole core messaging contract, complementing the existing relayer system. As the Executor network grows, developers get the advantage of broader chain support without having to custom-build their relayers for those environments. Just like the standard relayer, the Executor remains trust-minimized – an execution provider cannot violate the security of the message, and their signed quote simply helps ensure they are paid for the service.
For more technical details, see the [open-source example Executor implementation](https://github.com/wormholelabs-xyz/example-messaging-executor){target=\_blank}. It explains how quotes, requests, and the off-chain API function within the Executor system.
### Standard Relayer
The standard relayer refers to the Wormhole-operated relayer network available out of the box for EVM chains. This decentralized network of relayer nodes, run by Wormhole Contributors, automatically picks up eligible messages and delivers them to the destination chain. Importantly, integrators do not need to operate any backend infrastructure: interaction happens entirely through on-chain contracts. On the source chain, a contract calls the Wormhole relayer contract’s send function (e.g., [`sendPayloadToEvm`](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayer.sol#L86){target=\_blank}) to request delivery, specifying the target chain and paying the associated fee. Then the relayer network transports the VAA and calls the target contract on the destination chain to pass along the message data. The target contract must implement a standard interface (such as [`IWormholeReceiver`](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeReceiver.sol#L8){target=\_blank}) to handle the incoming message.
Using the standard relayer provides two main benefits: ease of integration and no infrastructure to maintain. Developers do not need to run servers or monitor the Guardian network; everything is handled by the relayer service. This lowers operational costs and complexity for cross-chain messaging. Sending a cross-chain message becomes almost as simple as emitting an event or calling a function, and receiving it is comparable to handling a callback. Because relayers cannot alter VAAs, the security model remains trust-minimized: Wormhole’s Guardian signatures provide full verification, and the relayer only affects availability.
**Trade-offs**
- All computation must be performed on-chain; no off-chain logic supported.
- Cannot handle advanced workflows such as conditional logic, multi-step processes, or gas-heavy computations.
- Limited to EVM-compatible blockchains (no support for Solana, Sui, etc.).
- Requires fees to cover destination chain gas and a service charge, paid on the source chain.
!!!note
Wormhole provides other relaying options for specific use cases, such as Native Token Transfers (NTT).
## Custom Relayer
For projects with special requirements or the need for complete control, custom relaying is an option. This involves building and running a relayer service tailored to the application. A custom relayer typically runs as a backend service that listens for specific VAAs from the Wormhole network (often via a [Spy](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/spy/){target=\_blank}) and then submits transactions to the destination chain when relevant messages are observed. Because Wormhole VAAs are public and trustless, anyone can run a relayer — an integrator could even operate a private relayer that only handles their own protocol’s messages.
The primary motivation for choosing this route is flexibility and optimization; another reason may be specific chains where a Wormhole relayer is still not available. With an off-chain component, developers can:
- Apply conditional logic like aggregating multiple messages and relaying them in a single transaction (batching).
- Trigger delivery logic (e.g., timing, price feeds, external signals) before delivery.
- Perform computations off-chain to reduce on-chain gas costs.
- Design custom incentive structures (e.g., funded by a protocol treasury or user-paid fees).
- Enhance the user experience with optimizations specific to an app.
**Trade-offs**
- Must run 24/7 with dedicated infrastructure (servers or cloud functions).
- Requires ongoing DevOps and monitoring to ensure availability.
- More complex development: integrators must handle Wormhole messages securely and always verify VAAs.
- May need to manage cross-chain fee payments.
- Provides maximum flexibility, but with higher operational responsibility.
To simplify development, Wormhole provides the [Relayer Engine](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/relayer-engine){target=\_blank}, a tool that abstracts boilerplate tasks such as listening to Guardians, parsing messages, and handling retries. Developers can then focus on application-specific logic, such as filtering relevant VAAs, forwarding to multiple chains, or applying off-chain checks.
## Next Steps
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Spy**
---
Discover Wormhole's Spy daemon, which subscribes to gossiped messages in the Guardian Network, including VAAs and Observations, with setup instructions.
[:custom-arrow: Learn More About the Spy](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/spy/)
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Build with Wormhole Relayers**
---
Learn how to use Wormhole-deployed relayer configurations for seamless cross-chain messaging between contracts on different EVM blockchains without off-chain deployments.
[:custom-arrow: Get Started with Wormhole Relayers](/docs/products/messaging/guides/wormhole-relayers/)
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Run a Custom Relayer**
---
Learn how to build and configure your own off-chain custom relaying solution to relay Wormhole messages for your applications using the Relayer Engine.
[:custom-arrow: Get Started with Custom Relayers](/docs/protocol/infrastructure-guides/run-relayer/)
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/infrastructure/spy.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Spy
description: Discover Wormhole's Spy daemon, which subscribes to gossiped messages in the Guardian Network, including VAAs and Observations, with setup instructions.
categories: Basics
---
# Spy
In Wormhole's ecosystem, the _Spy_ is a daemon, a continuously running background process that monitors messages within the Guardian Network. Unlike Guardians, a Spy doesn't perform validation; instead, it serves as an interface for observing the network's message traffic, enabling applications and users to access live data transmitted over Wormhole.
The primary purpose of a Spy is to subscribe to the gossiped messages across the Guardian Network, tracking key message types that allow integrators and applications to monitor real-time network activity without directly engaging in consensus operations.
This page provides a comprehensive guide to where the Spy fits within the Wormhole network, describing the key features and role in facilitating multichain processes.
## Key Features
- **Real-time monitoring of Wormhole messages**: The Spy allows users to observe Wormhole messages as they are published across supported chains in near real-time.
- **Filterable and observable message streams**: Users can filter message streams by chain, emitter, and other criteria, making it easier to track specific contracts or categories of interest.
- **Integration-friendly event streaming**: The Spy exposes gRPC and WebSocket interfaces, making it easy to integrate message observation into custom tooling, dashboards, or indexing services.
- **Support for multiple message protocols**: It can observe messages from different Wormhole messaging protocols (WTT, CCTP, NTT, etc.), providing broad coverage of cross-chain activity.
- **Lightweight and infrastructure-ready**: The Spy is designed to run as part of indexing or backend services, not requiring validator-level infrastructure.
## Integrator Use Case
The Spy provides a valuable mechanism for integrators to observe real-time network activity in the Guardian Network without directly engaging in validation or consensus. By running a Spy, integrators can track multichain events and message flows — such as VAAs, observations, and Guardian heartbeats — to monitor network activity essential to their applications.
This monitoring capability is especially beneficial for applications that need immediate insights into multichain data events. Integrators can run a Spy to ensure their applications are promptly informed of message approvals, observations, or Guardian liveness signals, supporting timely and responsive app behavior without additional overhead on network resources.
## Observable Message Categories
A Spy can access the following categories of messages shared over the gossip protocol:
- **[Verifiable Action Approvals (VAAs)](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas/){target=\_blank}**: Packets of multichain data.
- The Spy can detect whether a VAA has been approved by the Guardian Network, making it a valuable tool for applications needing real-time multichain verification.
- **[Observations](/docs/products/reference/glossary/#observation){target=\_blank}**: Emitted by Wormhole's core contracts, observations are picked up by the Guardians and relayed across the network.
- A Spy allow users to monitor these messages, adding transparency and insight into blockchain events.
- **[Guardian heartbeats](/docs/products/reference/glossary/#heartbeat){target=\_blank}**: Heartbeat messages represent Guardian node status.
- By monitoring heartbeats, a Spy can signal the liveness and connectivity of Guardians in the network.
## Additional Resources
- :octicons-code-16:{ .lg .middle } **Spy Source Code**
---
To see the source code for the Go implementation of the Spy, visit the `wormhole` repository on GitHub.
[:custom-arrow: View the Source Code](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/node/cmd/spy/spy.go){target=\_blank}
- :octicons-code-16:{ .lg .middle } **Alternative Implementation**
---
Visit the `beacon` repository on GitHub to learn more about Beacon, an alternative highly available, reduced-latency version of the Wormhole Spy.
[:custom-arrow: Get Started with Pyth Beacon](https://github.com/pyth-network/beacon)
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Discover Wormhole Queries**
---
For an alternative option to on-demand access to Guardian-attested multichain data, see the Wormhole Queries page. Queries provide a simple, REST endpoint style developer experience.
[:custom-arrow: Explore Queries](/docs/products/queries/overview/)
## Next Steps
- :octicons-code-16:{ .lg .middle } **Run a Spy**
---
Learn how to run the needed infrastructure to spin up a Spy daemon locally and subscribe to a stream of Verifiable Action Approvals (VAAs).
[:custom-arrow: Spin Up a Spy](/docs/protocol/infrastructure-guides/run-spy/){target=\_blank}
- :octicons-code-16:{ .lg .middle } **Use Queries**
---
For access to real-time network data without infrastructure overhead, follow this guide and use Wormhole Query to construct a query, make a request, and verify the response.
[:custom-arrow: Get Started with Queries](/docs/products/queries/guides/use-queries/)
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/infrastructure/vaas.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: VAAs
description: Learn about Verified Action Approvals (VAAs) in Wormhole, their structure, validation, and role in cross-chain communication.
categories: Basics
---
# Verified Action Approvals
Verified Action Approvals (VAAs) are Wormhole's core messaging primitive. They are packets of cross-chain data emitted whenever a cross-chain application contract interacts with the Core Contract.
[Guardians](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/guardians/){target=\_blank} validate messages emitted by contracts before sending them to the target chain. Once a majority of Guardians agree the message is valid, they sign a keccak256 hash of the message body.
The message is wrapped up in a structure called a VAA, which combines the message with the Guardian signatures to form a proof.
VAAs are uniquely indexed by the (`emitter_chain`, `emitter_address`, `sequence`) tuple. To obtain a VAA, one can query the [Wormholescan API](https://docs.wormholescan.io/){target=\_blank} with this information.
The `sequence` field depends on the final ordering of blocks on the emitter chain. When a lower consistency level is chosen (i.e., not waiting for finality), there is a chance that chain reorganizations could lead to multiple, different VAAs appearing for what looks like the “same” message on the user side.
The tuple (`emitter_chain`, `emitter_address`, `sequence`) can only be considered unique if the chain does not undergo a reorg and the block containing the message has effectively reached finality. However, there is always a small chance of an extended reorg that could invalidate or alter a previously emitted sequence number.
## VAA Format
The basic VAA consists of header and body components described as follows:
- **Header**: Holds metadata about the current VAA, the Guardian set that is currently active, and the list of signatures gathered so far.
- **`version` ++"byte"++**: The VAA Version.
- **`guardian_set_index` ++"u32"++**: Indicates which Guardian set is signing.
- **`len_signatures` ++"u8"++**: The number of signatures stored.
- **`signatures` ++"[]signature"++**: The collection of Guardian signatures.
Where each `signature` is:
- **`index` ++"u8"++**: The index of this Guardian in the Guardian set.
- **`signature` ++"[65]byte"++**: The ECDSA signature.
- **Body**: _deterministically_ derived from an on-chain message. Any two Guardians processing the same message must derive the same resulting body to maintain a one-to-one relationship between VAAs and messages to avoid double-processing messages.
- **`timestamp` ++"u32"++**: The timestamp of the block this message was published in.
- `nonce` ++"u32"++.
- **`emitter_chain` ++"u16"++**: The id of the chain that emitted the message.
- **`emitter_address` ++"[32]byte"++**: The contract address (Wormhole formatted) that called the Core Contract.
- **`sequence` ++"u64"++**: The auto-incrementing integer that represents the number of messages published by this emitter.
- **`consistency_level` ++"u8"++**: The consistency level (finality) required by this emitter.
- **`payload` ++"[]byte"++**: Arbitrary bytes containing the data to be acted on.
The deterministic nature of the body is only strictly true once the chain's state is finalized. If a reorg occurs, and a transaction that previously appeared in block X is replaced by block Y, Guardians observing different forks may generate different VAAs for what the emitter contract believes is the same message. This scenario is less likely once a block is sufficiently buried, but it can still happen if you choose a faster (less finalized) consistency level
The body contains relevant information for entities, such as contracts or other systems, that process or utilize VAAs. When a function like `parseAndVerifyVAA` is called, the body is returned, allowing verification of the `emitterAddress` to determine if the VAA originated from a trusted contract.
Because VAAs have no destination, they are effectively multicast. Any Core Contract on any chain in the network will verify VAAs as authentic. If a VAA has a specific destination, relayers are responsible for appropriately completing that delivery.
## Consistency and Finality
The consistency level determines whether Guardians wait for a chain's final commitment state or issue a VAA sooner under less-final conditions. This choice is especially relevant for blockchains without instant finality, where the risk of reorganization remains until a block is deeply confirmed.
Guardian watchers are specialized processes that monitor each blockchain in real-time. They enforce the selected consistency level by deciding whether enough commitment has been reached before signing and emitting a VAA. Some chains allow only one commitment level (effectively final), while others let integrators pick between near-final or fully finalized states. Choosing a faster option speeds up VAA production but increases reorg risk. A more conservative option takes longer but reduces the likelihood of rollback.
## Signatures
The body of the VAA is hashed twice with `keccak256` to produce the signed digest message.
```js
// hash the bytes of the body twice
digest = keccak256(keccak256(body))
// sign the result
signature = ecdsa_sign(digest, key)
```
!!!tip "Hash vs. double hash"
Different implementations of the ECDSA signature validation may apply a keccak256 hash to the message passed, so care must be taken to pass the correct arguments.
For example, the [Solana secp256k1 program](https://solana.com/docs/core/programs#secp256k1-program){target=\_blank} will hash the message passed. In this case, the argument for the message should be a single hash of the body, not the twice-hashed body.
## Payload Types
Different applications built on Wormhole may specify a format for the payloads attached to a VAA. This payload provides information on the target chain and contract so it can take action (e.g., minting tokens to a receiver address).
### Token Transfer
Many bridges use a lockup/mint and burn/unlock mechanism to transfer tokens between chains. Wormhole's generic message-passing protocol handles the routing of lock and burn events across chains to ensure Wormhole's Wrapped Token Transfer (WTT) is chain-agnostic and can be rapidly integrated into any network with a Wormhole contract.
Transferring tokens from the sending chain to the destination chain requires the following steps:
1. Lock the token on the sending chain.
2. The sending chain emits a message as proof the token lockup is complete.
3. The destination chain receives the message confirming the lockup event on the sending chain.
4. The token is minted on the destination chain.
The message the sending chain emits to verify the lockup is referred to as a transfer message and has the following structure:
- **`payload_id` ++"u8"++**: The ID of the payload. This should be set to `1` for a token transfer.
- **`amount` ++"u256"++**: Amount of tokens being transferred.
- **`token_address` ++"u8[32]"++**: Address on the source chain.
- **`token_chain` ++"u16"++**: Numeric ID for the source chain.
- **`to` ++"u8[32]"++**: Address on the destination chain.
- **`to_chain` ++"u16"++**: Numeric ID for the destination chain.
- **`fee` ++"u256"++**: Portion of amount paid to a relayer.
This structure contains everything the destination chain needs to learn about a lockup event. Once the destination chain receives this payload, it can mint the corresponding asset.
Note that the destination chain is agnostic regarding how the tokens on the sending side were locked. They could have been burned by a mint or locked in a custody account. The protocol relays the event once enough Guardians have attested to its existence.
### Attestation
While the destination chain can trust the message from the sending chain to inform it of token lockup events, it has no way of verifying the correct token is locked up. To solve this, WTT supports token attestation.
To create a token attestation, the sending chain emits a message containing metadata about a token, which the destination chain may use to preserve the name, symbol, and decimal precision of a token address.
The message format for token attestation is as follows:
- **`payload_id` ++"u8"++**: The ID of the payload. This should be set to `2` for an attestation.
- **`token_address` ++"[32]byte"++**: Address of the originating token contract.
- **`token_chain` ++"u16"++**: Chain ID of the originating token.
- **`decimals` ++"u8"++**: Number of decimals this token should have.
- **`symbol` ++"[32]byte"++**: Short name of asset.
- **`name` ++"[32]byte"++**: Full name of asset.
#### Attestation Tips
Be aware of the following considerations when working with attestations:
- Attestations use a fixed-length byte array to encode UTF8 token name and symbol data. Because the byte array is fixed length, the data contained may truncate multibyte Unicode characters.
- When sending an attestation VAA, it is recommended to send the longest UTF8 prefix that doesn't truncate a character and then right-pad it with zero bytes.
- When parsing an attestation VAA, it is recommended to trim all trailing zero bytes and convert the remainder to UTF-8 via any lossy algorithm.
- Be mindful that different on-chain systems may have different VAA parsers, resulting in different names/symbols on different chains if the string is long or contains invalid UTF8.
- Without knowing a token's decimal precision, the destination chain cannot correctly mint the number of tokens when processing a transfer. For this reason, WTT requires an attestation for each token transfer.
### Token Transfer with Message
The Token Transfer with Message data structure is identical to the token-only data structure, except for the following:
- **`fee` field**: Replaced with the `from_address` field.
- **`payload` field**: Is added containing arbitrary bytes. A dApp may include additional data in this arbitrary byte field to inform some application-specific behavior.
This VAA type was previously known as Contract Controlled Transfer and is also sometimes referred to as a `payload3` message. The Token Transfer with Message data sructure is as follows:
- **`payload_id` ++"u8"++**: The ID of the payload. This should be set to `3` for a token transfer with message.
- **`amount` ++"u256"++**: Amount of tokens being transferred.
- **`token_address` ++"u8[32]"++**: Address on the source chain.
- **`token_chain` ++"u16"++**: Numeric ID for the source chain.
- **`to` ++"u8[32]"++**: Address on the destination chain.
- **`to_chain` ++"u16"++**: Numeric ID for the destination chain.
- **`from_address` ++"u8[32]"++**: Address that called WTT on the source chain.
- **`payload` ++"[]byte"++**: Message, arbitrary bytes, app-specific.
### Governance
Governance VAAs don't have a `payload_id` field like the preceding formats. Instead, they trigger an action in the deployed contracts (for example, an upgrade).
#### Action Structure
Governance messages contain pre-defined actions, which can target the various Wormhole modules currently deployed on-chain. The structure includes the following fields:
- **`module` ++"u8[32]"++**: Contains a right-aligned module identifier.
- **`action` ++"u8"++**: Predefined governance action to execute.
- **`chain` ++"u16"++**: Chain the action is targeting. This should be set to `0` for all chains.
- **`args` ++"any"++**: Arguments to the action.
Below is an example message containing a governance action triggering a code upgrade to the Solana Core Contract. The module field here is a right-aligned encoding of the ASCII Core, represented as a 32-byte hex string.
```js
module: 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000436f7265
action: 1
chain: 1
new_contract: 0x348567293758957162374959376192374884562522281937446234828323
```
#### Actions
The meaning of each numeric action is pre-defined and documented in the Wormhole design documents. For each application, the relevant definitions can be found via these links:
- [Core governance actions](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/whitepapers/0002_governance_messaging.md){target=\_blank}
- [WTT governance actions](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/whitepapers/0003_token_bridge.md){target=\_blank}
## Lifetime of a Message
Anyone can submit a VAA to the target chain. Guardians typically don't perform this step to avoid transaction fees. Instead, applications built on top of Wormhole can acquire a VAA via the Guardian RPC and submit it in a separate flow.
With the concepts now defined, it is possible to illustrate a full flow for message passing between two chains. The following stages demonstrate each step of processing that the Wormhole network performs to route a message.
1. **A message is emitted by a contract running on Chain A**: Any contract can emit messages, and the Guardians are programmed to observe all chains for these events. Here, the Guardians are represented as a single entity to simplify the graphics, but the observation of the message must be performed individually by each of the 19 Guardians.
2. **Signatures are aggregated**: Guardians independently observe and sign the message. Once enough Guardians have signed the message, the collection of signatures is combined with the message and metadata to produce a VAA.
3. **VAA submitted to target chain**: The VAA acts as proof that the Guardians have collectively attested the existence of the message payload. The VAA is submitted (or relayed) to the target chain to be processed by a receiving contract and complete the final step.

## Next Steps
- :octicons-book-16:{ .lg .middle } **Guardians**
---
Explore Wormhole's Guardian Network, a decentralized system for secure, scalable cross-chain communication across various blockchain ecosystems.
[:custom-arrow: Learn About Guardians](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/guardians/)
- :octicons-tools-16:{ .lg .middle } **Wormhole Relayer**
---
Explore this guide to using Wormhole-deployed relayers to send and receive messages using VAAs.
[:custom-arrow: Build with Wormhole Relayer](/docs/products/messaging/guides/wormhole-relayers/)
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/introduction.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Introduction to Wormhole
description: Wormhole is a protocol for seamless communication between blockchains, enabling cross-chain applications and integrations.
categories: Basics
---
# Introduction to Wormhole
In the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain technology, interoperability between different blockchains remains a significant challenge. Developers often face hurdles in creating applications that can seamlessly operate across multiple blockchains, limiting innovation and the potential of decentralized ecosystems.
Wormhole addresses this problem by providing a _generic message-passing_ protocol that enables secure and efficient communication between blockchains. By allowing data and asset transfers across various blockchain networks, Wormhole breaks down the walls that traditionally separate these ecosystems.
Wormhole is distinguished by its focus on robust security, scalability, and transparency. The protocol is supported by a decentralized network of validators that ensure the integrity of every cross-chain transaction. This, combined with Wormhole’s proven performance in real-world applications, gives developers a dependable platform to create and scale multichain applications confidently.
!!! note
The above is an oversimplified illustration of the protocol; details about the architecture and components are available on the [architecture page](/docs/protocol/architecture/){target=\_blank}.
Wormhole allows developers to leverage the strengths of multiple blockchain ecosystems without being confined to one. This means applications can benefit from the unique features of various networks—such as Solana's high throughput, Ethereum's security, and Cosmos's interoperability while maintaining a unified, efficient user experience.
This page introduces the key concepts and components necessary to understand how Wormhole enables fast, secure, and scalable cross-chain communication.
## What Problems Does Wormhole Solve?
Interoperability is a critical challenge in the rapidly evolving blockchain landscape. Individual blockchains are often isolated, limiting the potential for integrated applications operating across multiple ecosystems. Wormhole solves this problem by enabling seamless communication between blockchains, allowing developers to create multichain applications that can leverage the unique features of each network.
Critical problems Wormhole addresses include:
- **Blockchain isolation**: Wormhole connects disparate blockchains, enabling the transfer of assets, data, and governance actions across networks.
- **Cross-chain complexity**: By abstracting the complexities of cross-chain communication, Wormhole makes it easier for developers to build and deploy cross-chain applications.
- **Security and decentralization**: Wormhole prioritizes security through a decentralized Guardian network that validates and signs messages, ensuring the integrity of cross-chain interactions.
## What Does Wormhole Offer?
Wormhole provides a suite of tools and protocols that support a wide range of use cases:
- **Cross-chain messaging**: Securely transfer arbitrary data between blockchains, enabling the development of cross-chain decentralized applications.
- **Asset transfers**: Facilitate the movement of tokens across supported chains with ease, powered by protocols built on Wormhole like [Portal](https://portalbridge.com/){target=\_blank}.
- **Developer tools**: Leverage Wormhole’s [TypeScript SDK](/docs/tools/typescript-sdk/get-started/){target=\_blank}, [Wormholescan](https://wormholescan.io/){target=\_blank}, and the [Wormholescan API](https://wormholescan.io/#/developers/api-doc){target=\_blank} and documentation to build and deploy cross-chain applications quickly and efficiently.
## What Isn't Wormhole?
- **Wormhole is _not_ a blockchain**: It acts as a communication layer that connects different blockchains, enabling them to interact without being a blockchain itself.
- **Wormhole is _not_ a token bridge**: While it facilitates token transfers, Wormhole also supports a wide range of cross-chain applications, making it much more versatile than a typical bridge.
## Use Cases of Wormhole
Consider the following examples of potential applications enabled by Wormhole:
- **Cross-chain exchange**: Using [Wormhole Connect](/docs/products/connect/overview/){target=\_blank}, developers can build exchanges that allow deposits from any Wormhole-connected chain, significantly increasing liquidity access.
- [**Cross-chain governance**](https://wormhole.com/blog/stake-for-governance-guide){target=\_blank}: Projects with communities spread across multiple blockchains can use Wormhole to relay votes from each chain to a designated governance chain, enabling unified decision-making through combined proposals.
- **Cross-chain game**: Games can be developed on a performant network like Solana, with rewards issued on another network, such as Ethereum.
## Explore
Discover more about the Wormhole ecosystem, components, and protocols:
- **[Architecture](/docs/protocol/architecture/){target=\_blank}**: Explore the components of the protocol.
- **[Protocol Specifications](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/tree/main/whitepapers){target=\_blank}**: Learn about the protocols built on top of Wormhole.
## Demos
Demos offer more realistic implementations than tutorials:
- **[Wormhole Scaffolding](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-scaffolding){target=\_blank}**: Quickly set up a project with the Scaffolding repository.
- **[Demo Tutorials](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/demo-tutorials){target=\_blank}**: Explore various demos that showcase Wormhole's capabilities across different blockchains.
!!! note
Wormhole Integration Complete?
Let us know so we can list your project in our ecosystem directory and introduce you to our global, multichain community!
**[Reach out now!](https://forms.clickup.com/45049775/f/1aytxf-10244/JKYWRUQ70AUI99F32Q){target=\_blank}**
## Supported Networks by Product
Wormhole supports a growing number of blockchains. Check out the [Supported Networks by Product](/docs/products/reference/supported-networks/){target=\_blank} page to see which networks are supported for each Wormhole product.
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/protocol/security.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Security
description: Explore Wormhole's security features, including the Guardian network, governance, monitoring, open-source development, and bug bounty programs.
categories: Basics
---
# Security
## Core Security Assumptions
At its core, Wormhole is secured by a network of [Guardian](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/guardians/){target=\_blank} nodes that validate and sign messages. If a super majority (e.g., 13 out of 19) of Guardians sign the same message, it can be considered valid. A smart contract on the target chain will verify the signatures and format of the message before approving any transaction.
- Wormhole's core security primitive is its signed messages (signed [VAAs](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/vaas/){target=\_blank}).
- The Guardian network is currently secured by a collection of 19 of the world's top [validator companies](https://wormhole-foundation.github.io/wormhole-dashboard/#/?endpoint=Mainnet){target=\_blank}.
- Guardians produce signed state attestations (signed VAAs) when requested by a Core Contract integrator.
- Every Guardian runs full nodes (rather than light nodes) of every blockchain in the Wormhole network, so if a blockchain suffers a consensus attack or hard fork, the blockchain will disconnect from the network rather than potentially produce invalid signed VAAs.
- Any Signed VAA can be verified as authentic by the Core Contract of any other chain.
- [Relayers](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/relayer/){target=\_blank} are considered untrusted in the Wormhole ecosystem.
In summary:
- **Core integrators aren't exposed to risk from chains and contracts they don't integrate with**.
- By default, you only trust Wormhole's signing process and the core contracts of the chains you're on.
- You can expand your contract and chain dependencies as you see fit.
Core assumptions aside, many other factors impact the real-world security of decentralized platforms. Here is more information on additional measures that have been put in place to ensure the security of Wormhole.
## Guardian Network
Wormhole is an evolving platform. While the Guardian set currently comprises 19 validators, this is a limitation of current blockchain technology.
### Governance
Governance is the process through which contract upgrades happen. Guardians manually vote on governance proposals that originate inside the Guardian Network and are then submitted to ecosystem contracts.
This means that governance actions are held to the same security standard as the rest of the system. A two-thirds supermajority of the Guardians is required to pass any governance action.
Governance messages can target any of the various wormhole modules, including the core contracts and all currently deployed Wrapped Token Transfers (WTT) contracts. When a Guardian signs such a message, its signature implies a vote on the action in question. Once more than two-thirds of the Guardians have signed, the message and governance action are considered valid.
All governance actions and contract upgrades have been managed via Wormhole's on-chain governance system.
Via governance, the Guardians can:
- Change the current Guardian set.
- Expand the Guardian set.
- Upgrade ecosystem contract implementations.
The governance system is fully open source in the core repository. See the [Open Source section](#open-source){target=\_blank} for contract source.
## Monitoring
A key element of Wormhole's defense-in-depth strategy is that each Guardian is a highly competent validator company with its own in-house processes for running, monitoring, and securing blockchain operations. This heterogeneous approach to monitoring increases the likelihood that fraudulent activity is detected and reduces the number of single failure points in the system.
Guardians are not just running Wormhole validators; they're running validators for every blockchain inside of Wormhole as well, which allows them to perform monitoring holistically across decentralized computing rather than just at a few single points.
Guardians monitor:
- **Block production and consensus of each blockchain**: If a blockchain's consensus is violated, it will be disconnected from the network until the Guardians resolve the issue.
- **Smart contract level data**: Via processes like the Governor, Guardians constantly monitor the circulating supply and token movements across all supported blockchains.
- **Guardian level activity**: The Guardian Network functions as an autonomous decentralized computing network, ensuring independent security measures across its validators.
## Asset Layer Protections
One key strength of the Wormhole ecosystem is the Guardians’ ability to validate and protect the integrity of assets across multiple blockchains.
To enforce the Wormhole Asset Layer’s core protections, the Global Accountant tracks the total circulating supply of all Wormhole assets across all chains, preventing any blockchain from bridging assets that could violate the supply invariant.
In addition to the Global Accountant, Guardians may only sign transfers that do not violate the requirements of the Governor. The [Governor](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/whitepapers/0007_governor.md){target=\_blank} tracks inflows and outflows of all blockchains and delays suspicious transfers that may indicate an exploit.
## Open Source
Wormhole builds in the open and is always open source.
- **[Wormhole core repository](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole){target=\_blank}**
- **[Wormhole Foundation GitHub organization](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation){target=\_blank}**
- **[Wormhole contract deployments](/docs/protocol/infrastructure/core-contracts/){target=\_blank}**
## Audits
Wormhole has been heavily audited, with _29 third-party audits completed_ and more started. Audits have been performed by the following firms:
- [Trail of Bits](https://www.trailofbits.com/){target=\_blank}
- [Neodyme](https://neodyme.io/en/){target=\_blank}
- [Kudelski](https://kudelskisecurity.com/){target=\_blank}
- [OtterSec](https://osec.io/){target=\_blank}
- [Certik](https://www.certik.com/){target=\_blank}
- [Hacken](https://hacken.io/){target=\_blank}
- [Zellic](https://www.zellic.io/){target=\_blank}
- [Coinspect](https://www.coinspect.com/){target=\_blank}
- [Halborn](https://www.halborn.com/){target=\_blank}
- [Cantina](https://cantina.xyz/welcome){target=\_blank}
All audits and final reports can be found in [security page of the GitHub Repo](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/SECURITY.md#3rd-party-security-audits){target=\blank}.
## Bug Bounties
Wormhole has one of the largest bug bounty programs in software development and has repeatedly shown commitment to engaging with the white hat community.
Wormhole runs a bug bounty program through [Immunefi](https://immunefi.com/bug-bounty/wormhole/){target=\blank} program, with a top payout of **5 million dollars**.
If you are interested in contributing to Wormhole security, please look at this section for [Getting Started as a White Hat](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/SECURITY.md#white-hat-hacking){target=\blank}, and follow the [Wormhole Contributor Guidelines](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md){target=\blank}.
For more information about submitting to the bug bounty programs, refer to the [Wormhole Immunefi page](https://immunefi.com/bug-bounty/wormhole/){target=\blank}.
## Learn More
The [SECURITY.md](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/SECURITY.md){target=\blank} from the official repository has the latest security policies and updates.
--- END CONTENT ---
## Shared Concepts from reference
The following section contains reference material for Wormhole, including chain IDs, canonical contract addresses, finality levels, and other advanced specs. While it may not be required for all use cases, it provides a deeper layer for advanced development work.
---
## List of Shared Concept Pages:
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/core-contract-evm.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/core-contract-solana.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/executor-addresses.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/relayer-contract.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/chain-ids.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/consistency-levels.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/contract-addresses.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/executor-addresses.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/supported-networks.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/testnet-faucets.md [type: reference]
Doc-Page: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/wormhole-formatted-addresses.md [type: reference]
## Full content for shared concepts:
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/core-contract-evm.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Core Contract (EVM)
description: Reference for the Wormhole Core contract on EVM chains. Covers the proxy structure, components, state variables, functions, events, and errors.
categories: Reference
---
# Core Contract (EVM)
The [Wormhole Core Contract on EVM](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank} chains is a proxy-based contract responsible for receiving and verifying Wormhole messages (VAAs). It implements the messaging interface and delegates logic to upgradeable implementation contracts.
## Structure Overview
The Wormhole Core system consists of a proxy contract and a modular implementation constructed through layered inheritance.
```text
Wormhole.sol (Proxy)
└── Implementation.sol
└── Governance.sol
├── Getters.sol
├── GovernanceStructs.sol
├── Messages.sol
├── Setters.sol
└── Structs.sol
```
**Key Components:**
- **Wormhole.sol**: The upgradeable proxy contract that delegates all logic to `Implementation.sol`.
- **Implementation.sol**: The main logic contract, which handles message publication and initialization. Inherits from Governance.sol.
- **Governance.sol**: Core governance logic for processing upgrades, setting fees, and updating the Guardian set. Also responsible for verifying governance VAAs and performing privileged actions.
- **Getters.sol**: Exposes view functions to access internal contract state, such as current Guardian sets, fees, and contract configuration.
- **GovernanceStructs.sol**: Provides structures and helpers for processing governance-related VAAs.
- **Messages.sol**: Handles VAA parsing and verification.
- **Setters.sol**: Contains internal functions for mutating contract state.
- **Structs.sol**: Defines core data structures like GuardianSet and VM (VAA Message) used across multiple modules.
## State Variables
- **`provider` ++"Structs.Provider"++**: Holds metadata like `chainId`, `governanceChainId`, and `governanceContract`. This is a nested struct.
- **`guardianSets` ++"mapping(uint32 => GuardianSet)"++**: Mapping of all Guardian sets by index.
- **`guardianSetIndex` ++"uint32"++**: Index of the currently active Guardian set.
- **`guardianSetExpiry` ++"uint32"++**: How long a Guardian set remains valid after it's replaced (in seconds).
- **`sequences` ++"mapping(address => uint64)"++**: Tracks message sequences per emitter (used to enforce message ordering).
- **`consumedGovernanceActions` ++"mapping(bytes32 => bool)"++**: Used to prevent governance VAAs from being reused (replay protection).
- **`initializedImplementations` ++"mapping(address => bool)"++**: Tracks which implementation addresses have been initialized (for upgrade safety).
- **`messageFee` ++"uint256"++**: The amount (in native gas token) required to post a message. Set via governance.
- **`evmChainId` ++"uint256"++**: The actual EVM chain ID (e.g., 1 for Ethereum, 10 for Optimism). Used in fork recovery.
## Events
### LogMessagePublished
Emitted when a message is published via `publishMessage`. *(Defined in [Implementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event LogMessagePublished(
address indexed sender,
uint64 sequence,
uint32 nonce,
bytes payload,
uint8 consistencyLevel
)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`sender` ++"address"++
Address that called `publishMessage`.
---
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
The sequence number of the message.
---
`nonce` ++"uint32"++
The provided nonce.
---
`payload` ++"bytes"++
The payload that was published.
---
`consistencyLevel` ++"uint8"++
Finality level requested.
### ContractUpgraded
Emitted when the Core Contract is upgraded to a new implementation via governance. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event ContractUpgraded(
address indexed oldContract,
address indexed newContract
)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`oldContract` ++"address"++
The address of the previous implementation.
---
`newContract` ++"address"++
The address of the new implementation.
### GuardianSetAdded
Emitted when a new Guardian set is registered via governance. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event GuardianSetAdded(
uint32 indexed index
)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`index` ++"uint32"++
Index of the newly added Guardian set.
### LogGuardianSetChanged
Emitted when the active Guardian set is changed. *(Defined in [State.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/State.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event LogGuardianSetChanged(
uint32 oldGuardianIndex,
uint32 newGuardianIndex
)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`oldGuardianIndex` ++"uint32"++
The previous active Guardian set index.
---
`newGuardianIndex` ++"uint32"++
The new active Guardian set index.
## Functions
### publishMessage
Publishes a message to Wormhole's Guardian Network. *(Defined in [Implementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function publishMessage(
uint32 nonce,
bytes memory payload,
uint8 consistencyLevel
) public payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`nonce` ++"uint32"++
Custom sequence identifier for the emitter.
---
`payload` ++"bytes"++
Arbitrary user data to be included in the message.
---
`consistencyLevel` ++"uint8"++
Finality requirement for Guardian attestation (e.g., safe or finalized).
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Unique sequence number assigned to this message.
### getCurrentGuardianSetIndex
Returns the index of the currently active Guardian set. *(Defined in [Getters.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Getters.sol){target=\_blank})*
Each VAA includes the index of the Guardian set that signed it. This function allows contracts to retrieve the current index, ensuring the VAA is verified against the correct set.
```solidity
function getCurrentGuardianSetIndex() external view returns (uint32)
```
??? interface "Returns"
`index` ++"uint32"++
The index of the active Guardian set used to verify signatures.
### getGuardianSet
Retrieves metadata for a given Guardian set index. *(Defined in [Getters.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Getters.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function getGuardianSet(uint32 index) external view returns (address[] memory keys, uint32 expirationTime)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`index` ++"uint32"++
Guardian set index to query.
??? interface "Returns"
`keys` ++"address[]"++
Public keys of the guardians in this set.
---
`expirationTime` ++"uint32"++
Timestamp after which the Guardian set is considered expired.
### getGuardianSetExpiry
Returns the expiration time of a specific Guardian set index. *(Defined in [Getters.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Getters.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function getGuardianSetExpiry(uint32 index) external view returns (uint32)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`index` ++"uint32"++
The index of the Guardian set to query.
??? interface "Returns"
`expiry` ++"uint32"++
UNIX timestamp after which the set is no longer valid.
### messageFee
Returns the current fee (in native tokens) required to publish a message. *(Defined in [Getters.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Getters.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function messageFee() public view returns (uint256)
```
??? interface "Returns"
`fee` ++"uint256"++
Fee in Wei required to publish a message successfully. Must be sent as `msg.value`.
### nextSequence
Retrieves the next sequence number for a given emitter address. *(Defined in [Getters.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Getters.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function nextSequence(address emitter) external view returns (uint64)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`emitter` ++"address"++
The address for which the next sequence will be issued.
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
The next sequence number for the specified emitter.
### parseAndVerifyVM
Verifies signatures and parses a signed VAA. *(Defined in [Messages.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Messages.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function parseAndVerifyVM(bytes memory encodedVM)
external
view
returns (
VM memory vm,
bool valid,
string memory reason
)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`encodedVM` ++"bytes"++
Serialized signed VAA from Guardians.
??? interface "Returns"
`vm` ++"VM memory"++
Full parsed VAA contents
---
`valid` ++"bool"++
Whether the VAA is valid according to the current Guardian set.
---
`reason` ++"string"++
Reason for invalidity if `valid` is false (invalid).
### verifyVM
Performs low-level VAA signature verification. *(Defined in [Messages.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Messages.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function verifyVM(bytes memory encodedVM)
public view returns (bool isValid, string memory reason)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`encodedVM` ++"bytes"++
Serialized signed VAA to verify.
??? interface "Returns"
`isValid` ++"bool"++
`true` if the signatures are valid and meet the quorum.
---
`reason` ++"string"++
Explanation for failure if `isValid` is `false`.
### verifySignatures
Used to verify individual Guardian signatures against a VAA digest. *(Defined in [Messages.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Messages.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function verifySignatures(
bytes32 hash,
Structs.Signature[] memory signatures,
GuardianSet memory guardianSet
) public view returns (bool)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`hash` ++"bytes32"++
The message digest to verify.
---
`signatures` ++"Structs.Signature[]"++
An array of Guardian signatures.
---
`guardianSet` ++"GuardianSet memory"++
Guardian set to validate against.
??? interface "Returns"
`isValid` ++"bool"++
`true` if the required number of valid signatures is present.
### quorum
Returns the number of Guardian signatures required to reach quorum. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function quorum() public view returns (uint8)
```
??? interface "Returns"
`quorum` ++"uint8"++
Number of valid Guardian signatures required to reach consensus for VAA verification.
### chainId
Returns Wormhole chain ID used internally by the protocol. *(Defined in [Getters.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Getters.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function chainId() public view returns (uint16)
```
??? interface "Returns"
`id` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole-specific chain identifier.
### evmChainId
Returns the EVM chain ID (i.e., value from `block.chainid`). *(Defined in [Getters.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Getters.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function evmChainId() public view returns (uint256)
```
??? interface "Returns"
`id` ++"uint256"++
Native EVM chain ID for the current network.
## Errors
### Invalid Fee
Reverts when the message fee (`msg.value`) sent is not equal to the required fee returned by `messageFee()`. *(Defined in [Implementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Unsupported
Reverts on any call to the fallback function. The contract does not support arbitrary calls. *(Defined in [Implementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank})*
### The Wormhole Contract Does Not Accept Assets
Reverts when native tokens (ETH) are sent directly to the contract via the `receive()` function. *(Defined in [Implementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Already Initialized
Reverts when trying to call `initialize()` on an implementation that has already been initialized. *(Defined in [Implementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank}, via `initializer` modifier)*
### Unknown Chain ID
Reverts inside the `initialize()` function if the chain ID stored by the contract does not match any known Wormhole chain. *(Defined in [Implementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Implementation.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Invalid Fork
Reverts when attempting to perform a governance action intended only for forked chains on a non-forked chain. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Invalid Module
Reverts if the VAA’s module field doesn’t match the expected "Core" module. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Invalid Chain
Reverts if the VAA’s target chain doesn’t match the chain on which this contract is deployed. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### New Guardian Set is Empty
Reverts when trying to register a new Guardian set that has no keys. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Index Must Increase in Steps of 1
Reverts when the new Guardian set index is not exactly one greater than the current. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Not a Fork
Reverts when trying to recover chain ID on a non-forked chain. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Invalid EVM Chain
Reverts if the recovered chain ID doesn't match the current `block.chainid`. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Governance Action Already Consumed
Reverts when the same governance VAA is submitted more than once. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Wrong Governance Contract
Reverts when the governance VAA’s emitter address doesn't match the expected governance contract address. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Wrong Governance Chain
Reverts when the governance VAA’s emitter chain doesn't match the expected governance chain (Solana). *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Not Signed by Current Guardian Set
Reverts if the Guardian set index in the VAA doesn’t match the current Guardian set. *(Defined in [Governance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/ethereum/contracts/Governance.sol){target=\_blank})*
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/core-contract-solana.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Core Contract (Solana)
description: Reference for the Wormhole Core program on Solana. Covers architecture, PDA accounts, and instructions for posting, verifying, and processing VAAs.
categories: Reference
---
# Core Contract (Solana)
The [Wormhole Core Program on Solana](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/lib.rs){target=\_blank} is a native Solana program responsible for posting, verifying, and relaying Wormhole messages (VAAs). It implements core messaging functionality, Guardian set updates, and upgradeability.
## Structure Overview
The Wormhole Core program on Solana is implemented using modular Rust files. Logic is separated across instruction dispatch, account definitions, core types, and signature verification.
```text
lib.rs
├── instructions.rs
├── accounts.rs
├── api.rs
│ ├── post_message
│ ├── verify_signatures
│ ├── post_vaa
│ ├── upgrade_contract
│ └── upgrade_guardian_set
├── types.rs
└── vaa.rs
```
**Key Components:**
- **lib.rs**: Program entry point and instruction dispatcher. Registers all handlers and exposes the on-chain processor.
- **instructions.rs**: Defines the `WormholeInstruction` enum and maps it to individual instruction handlers.
- **accounts.rs**: Specifies the account constraints and validation logic for each instruction.
- **api.rs**: Contains the main logic for processing instructions such as message posting, VAA verification, upgrades, and governance actions.
- **types.rs**: Defines shared structs and enums used throughout the program, including configuration and `GuardianSet` formats.
- **vaa.rs**: Implements VAA parsing, hashing, and signature-related logic used to verify Wormhole messages.
- **error.rs** (not listed above): Defines custom error types used across the program for precise failure handling.
- **wasm.rs** (not listed above): Provides WebAssembly bindings for testing and external tooling; not used on-chain.
## State Accounts
Below are on-chain PDAs used to store persistent state for the core contract. All are derived using deterministic seeds with the program ID.
- **`bridge` ++"BridgeData"++**: Stores global config like the active Guardian set index, message fee, and Guardian set expiration time. (Derived at PDA seed `["Bridge"]`)
- **`guardianSets` ++"GuardianSetData"++**: Mapping of Guardian sets by index. Each Guardian set includes public key hashes and creation/expiration times. (Derived at PDA seed `["GuardianSet", index]`)
- **`sequences` ++"SequenceTracker"++**: Tracks the last sequence number used by each emitter, enforcing strict message ordering. (Derived at PDA seed `["Sequence", emitter]`)
- **`postedVAAs` ++"PostedVAAData"++**: Stores verified and finalized VAAs, preventing replay. (Derived at PDA seed `["PostedVAA", hash]`)
- **`claims` ++"ClaimData"++**: Tracks consumed governance VAAs to ensure replay protection. (Derived at PDA seed `["Claim", emitter, sequence]`)
- **`feeCollector` ++"FeeCollector"++**: Holds lamports collected via message fees, and can be drained via governance. (Derived at PDA seed `["fee_collector"]`)
## Instructions
### initialize
Initializes the Wormhole Core contract on Solana with a Guardian set and fee configuration. This should be called only once at deployment time. *(Defined in [api/initialize.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/initialize.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
initialize(
payer: Pubkey,
fee: u64,
guardian_set_expiration_time: u32,
initial_guardians: &[[u8; 20]]
)
```
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Bridge`**: PDA to store global configuration.
- **`GuardianSet`**: PDA for Guardian set at index 0.
- **`FeeCollector`**: PDA to collect message posting fees.
- **`Payer`**: Funds account creation.
- **`Clock`, `Rent`, `SystemProgram`**: Solana system accounts.
??? interface "Parameters"
`fee` ++"u64"++
Fee in lamports required to post messages.
---
`guardian_set_expiration_time` ++"u32"++
Time in seconds after which the Guardian set expires.
---
`initial_guardians` ++"[[u8; 20]]"++
List of Guardian public key hashes (Ethereum-style addresses).
### post_message
Posts a Wormhole message to the Solana Core contract. *(Defined in [api/post_message.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/post_message.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
PostMessage {
nonce: u32,
payload: Vec,
consistency_level: u8
}
```
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Bridge`**: PDA for global config.
- **`Message`**: PDA where the posted message will be stored.
- **`Emitter`**: The emitting account (must sign).
- **`Sequence`**: PDA tracking the emitter’s message sequence.
- **`Payer`**: Pays for account creation and fees.
- **`FeeCollector`**: PDA that collects message fees.
- **`Clock`, `Rent`, `SystemProgram`**: Solana system accounts.
??? interface "Parameters"
`nonce` ++"u32"++
Unique nonce to disambiguate messages with the same payload.
---
`payload` ++"Vec"++
The arbitrary message payload to be posted.
---
`consistency_level` ++"u8"++
Level of finality required before the message is processed.
`1` = Confirmed, `32` = Finalized.
### post_message_unreliable
Posts a Wormhole message without requiring reliable delivery. Used for lightweight publishing when finality isn't critical. *(Defined in [api/post_message.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/post_message.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
PostMessageUnreliable {
nonce: u32,
payload: Vec,
consistency_level: u8
}
```
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Bridge`**: PDA for global config.
- **`Message`**: PDA where the posted message will be stored.
- **`Emitter`**: The emitting account (must sign).
- **`Sequence`**: PDA tracking the emitter’s message sequence.
- **`Payer`**: Pays for account creation and fees.
- **`FeeCollector`**: PDA that collects message fees.
- **`Clock`, `Rent`, `SystemProgram`**: Solana system accounts.
??? interface "Parameters"
`nonce` ++"u32"++
Unique nonce to disambiguate messages with the same payload.
---
`payload` ++"Vec"++
The arbitrary message payload to be posted.
---
`consistency_level` ++"u8"++
Level of finality required before the message is processed. `1` = Confirmed, `32` = Finalized.
### verify_signatures
Verifies Guardian signatures over a VAA body hash. This is the first step in VAA processing and is required before posting the VAA. *(Defined in [api/verify_signature.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/verify_signature.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
VerifySignatures {
signers: [i8; 19]
}
```
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Payer`**: Pays for account creation and fees.
- **`GuardianSet`**: PDA holding the current Guardian set.
- **`SignatureSet`**: PDA that will store the verified signature data.
- **`InstructionsSysvar`**: Required to access prior instructions (e.g., secp256k1 sigverify).
- **`Rent`, `SystemProgram`**: Solana system accounts.
??? interface "Parameters"
`signers` ++"[i8; 19]"++
A mapping from Guardian index to its position in the instruction payload (or -1 if not present).
Used to correlate secp256k1 verify instructions with Guardian set entries.
### post_vaa
Finalizes a VAA after signature verification. This stores the message on-chain and marks it as consumed. *(Defined in [api/post_vaa.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/post_vaa.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
PostVAA {
version: u8,
guardian_set_index: u32,
timestamp: u32,
nonce: u32,
emitter_chain: u16,
emitter_address: [u8; 32],
sequence: u64,
consistency_level: u8,
payload: Vec
}
```
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`GuardianSet`**: PDA of the Guardian set used to verify the VAA.
- **`Bridge`**: Global Wormhole state.
- **`SignatureSet`**: Verified signature PDA (from verify_signatures).
- **`PostedVAA`**: PDA where the VAA will be stored.
- **`Payer`**: Funds the account creation.
- **`Clock`, `Rent`, `SystemProgram`**: Solana system accounts.
??? interface "Parameters"
`version` ++"u8"++
VAA protocol version.
---
`guardian_set_index` ++"u32"++
Index of the Guardian Set that signed this VAA.
---
`timestamp` ++"u32"++
The time the emitter submitted the message.
---
`nonce` ++"u32"++
Unique identifier for the message.
---
`emitter_chain` ++"u16"++
ID of the chain where the message originated.
---
`emitter_address` ++"[u8; 32]"++
Address of the contract or account that emitted the message.
---
`sequence` ++"u64"++
Monotonically increasing sequence number for the emitter.
---
`consistency_level` ++"u8"++
Required confirmation level before the message is accepted.
`1` = Confirmed, `32` = Finalized.
---
`payload` ++"Vec"++
Arbitrary data being transferred in the message.
### set_fees
Updates the message posting fee for the core bridge contract. *(Defined in [api/governance.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/governance.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
SetFees {}
```
This function is called via governance and requires a valid governance VAA. The VAA payload must contain the new fee value.
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Payer`**: Funds transaction execution.
- **`Bridge`**: PDA storing global Wormhole state.
- **`Message`**: The PostedVAA account containing the governance message.
- **`Claim`**: PDA that ensures this governance message hasn't been processed already.
- **`SystemProgram`**: Required by Solana for creating/initializing accounts.
### transfer_fees
Transfers the accumulated message posting fees from the contract to a specified recipient. *(Defined in [api/governance.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/governance.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
TransferFees {}
```
This function is triggered via a governance VAA and transfers the fee balance from the `FeeCollector` to the recipient address specified in the VAA payload.
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Payer`**: Funds transaction execution.
- **`Bridge`**: PDA storing global Wormhole state.
- **`Message`**: PostedVAA account containing the governance message.
- **`FeeCollector`**: PDA holding the accumulated fees.
- **`Recipient`**: The account that will receive the fees.
- **`Claim`**: PDA that ensures this governance message hasn't been processed already.
- **`Rent`, `SystemProgram`**: Standard Solana system accounts.
### upgrade_contract
Upgrades the deployed Wormhole program using a governance VAA. *(Defined in [api/governance.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/governance.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
UpgradeContract {}
```
This instruction allows authorized governance messages to trigger an upgrade of the on-chain Wormhole program logic to a new address.
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Payer`**: Funds transaction execution.
- **`Bridge`**: PDA storing global Wormhole state.
- **`Message`**: PostedVAA account containing the governance message.
- **`Claim`**: PDA that ensures this governance message hasn't been processed already.
- **`UpgradeAuthority`**: PDA with authority to perform the upgrade (seeded with "upgrade").
- **`Spill`**: Account that receives remaining funds from the upgrade buffer.
- **`NewContract`**: Account holding the new program data.
- **`ProgramData`**: Metadata account for the upgradable program.
- **`Program`**: Current program to be upgraded.
- **`Rent`, `Clock`**: System accounts used during the upgrade process.
- **`BPFLoaderUpgradeable`**: Solana system program for upgrades.
- **`SystemProgram`**: Required by Solana for creating/initializing accounts.
### upgrade_guardian_set
Upgrades the current Guardian set using a governance VAA. *(Defined in [api/governance.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/api/governance.rs){target=\_blank})*
```rust
UpgradeGuardianSet {}
```
This instruction replaces the active Guardian set with a new one, allowing the Wormhole network to rotate its validator keys securely through governance.
??? interface "Accounts"
- **`Payer`**: Funds transaction execution.
- **`Bridge`**: PDA storing global Wormhole state.
- **`Message`**: PostedVAA account containing the governance message.
- **`Claim`**: PDA that ensures this governance message hasn't been processed already.
- **`GuardianSetOld`**: Current (active) Guardian set PDA.
- **`GuardianSetNew`**: PDA for the newly proposed Guardian set.
- **`SystemProgram`**: Standard Solana system accounts.
## Errors
### GuardianSetMismatch
The Guardian set index does not match the expected value. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InstructionAtWrongIndex
The instruction was found at the wrong index. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InsufficientFees
Insufficient fees were provided to post the message. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidFeeRecipient
The recipient address does not match the one specified in the governance VAA. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidGovernanceAction
The action specified in the governance payload is invalid. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidGovernanceChain
The governance VAA was not emitted by a valid governance chain. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidGovernanceKey
The emitter address in the governance VAA is not the expected governance key. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidGovernanceModule
The module string in the governance VAA header is invalid. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidGovernanceWithdrawal
Fee withdrawal would cause the fee collector account to drop below rent-exempt balance. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidGuardianSetUpgrade
The Guardian set upgrade VAA is invalid (e.g., skipped index or mismatched current index). *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidHash
The hash computed from the VAA does not match the expected result. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidSecpInstruction
The SECP256k1 instruction used for signature verification is malformed. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### MathOverflow
An arithmetic overflow occurred during computation. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### PostVAAConsensusFailed
Not enough valid signatures were collected to achieve quorum. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### PostVAAGuardianSetExpired
The Guardian set used to verify the VAA has already expired. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### TooManyGuardians
The Guardian set exceeds the maximum allowed number of guardians. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### VAAAlreadyExecuted
The VAA has already been executed and cannot be processed again. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### VAAInvalid
The VAA is structurally invalid or fails to decode. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidPayloadLength
The payload length is incorrect or malformed. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
### EmitterChanged
The emitter address changed unexpectedly. *(Defined in [error.rs](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/solana/bridge/program/src/error.rs){target=\_blank})*
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/executor-addresses.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Executor Addresses
description: Reference list of deployed Executor contract addresses across integrations, including CCTP, NTT, WTT, and referrer variants.
categories: Reference
---
# Executor Addresses
## Executor
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x84EEe8dBa37C36947397E1E11251cA9A06Fc6F8a |
| Solana | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Aptos | 0x11aa75c059e1a7855be66b931bf340a2e0973274ac16b5f519c02ceafaf08a18 |
| Arbitrum | 0x3980f8318fc03d79033Bbb421A622CDF8d2Eeab4 |
| Avalanche | 0x4661F0E629E4ba8D04Ee90080Aee079740B00381 |
| Base | 0x9E1936E91A4a5AE5A5F75fFc472D6cb8e93597ea |
| Berachain | 0x0Dd7a5a32311b8D87A615Cc7f079B632D3d5e2D3 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0xeC8cCCD058DbF28e5D002869Aa9aFa3992bf4ee0 |
| Celo | 0xe6Ea5087c6860B94Cf098a403506262D8F28cF05 |
| CreditCoin | 0xd2e420188f17607Aa6344ee19c3e76Cf86CA7BDe |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0xd7717899cc4381033Bc200431286D0AC14265F78 |
| Ink | 0x3e44a5F45cbD400acBEF534F51e616043B211Ddd |
| Linea | 0x23aF2B5296122544A9A7861da43405D5B15a9bD3 |
| Mezo | 0x0f9b8E144Cc5C5e7C0073829Afd30F26A50c5606 |
| Moonbeam | 0x85D06449C78064c2E02d787e9DC71716786F8D19 |
| Optimism | 0x85B704501f6AE718205C0636260768C4e72ac3e7 |
| Polygon | 0x0B23efA164aB3eD08e9a39AC7aD930Ff4F5A5e81 |
| Scroll | 0xcFAdDE24640e395F5A71456A825D0D7C3741F075 |
| Seievm | 0x25f1c923fb7a5aefa5f0a2b419fc70f2368e66e5 |
| Sonic | 0x3Fdc36b4260Da38fBDba1125cCBD33DD0AC74812 |
| Sui | 0xdb0fe8bb1e2b5be628adbea0636063325073e1070ee11e4281457dfd7f158235 |
| Unichain | 0x764dD868eAdD27ce57BCB801E4ca4a193d231Aed |
| World Chain | 0x8689b4E6226AdC8fa8FF80aCc3a60AcE31e8804B |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x8345E90Dcd92f5Cf2FAb0C8E2A56A5bc2c30d896 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0xD0fb39f5a3361F21457653cB70F9D0C9bD86B66B |
| Solana | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Aptos | 0x139717c339f08af674be77143507a905aa28cbc67a0e53e7095c07b630d73815 |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xBF161de6B819c8af8f2230Bcd99a9B3592f6F87b |
| Avalanche | 0x4661F0E629E4ba8D04Ee90080Aee079740B00381 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x51B47D493CBA7aB97e3F8F163D6Ce07592CE4482 |
| Converge | 0xAab9935349B9c08e0e970720F6D640d5B91C293E |
| Fogo | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Mezo | 0x0f9b8E144Cc5C5e7C0073829Afd30F26A50c5606 |
| Monad | 0xC04dE634982cAdF2A677310b73630B7Ac56A3f65 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x5856651eB82aeb6979B4954317194d48e1891b3c |
| Plume | 0x8fc2FbA8F962fbE89a9B02f03557a011c335A455 |
| Seievm | 0x25f1c923Fb7A5aEFA5F0A2b419fC70f2368e66e5 |
| Sui | 0x4000cfe2955d8355b3d3cf186f854fea9f787a457257056926fde1ec977670eb |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x4d9525D94D275dEB495b7C8840b154Ae04cfaC2A |
## CCTP With Executor
=== "Mainnet v1"
| Ethereum | 0xeEFb36c4458dA7798742cf038C5c27E07aB9c51E |
| Solana | CXGRA5SCc8jxDbaQPZrmmZNu2JV34DP7gFW4m31uC1zs |
| Arbitrum | 0x55Dd4466BFec29527C54A72fd306efb54e5F7027 |
| Avalanche | 0xd331819478b74d8a7B8EA631118B4a4e50F6EbD1 |
| Aptos | 0x9f5ad7d5c2d067ca4abb6d8d6aba44c15596b71a1def8eb4596089b527bb2eb1 |
| Base | 0x08FEB1838C3d7F8509DA1EBb9a11a94c1f006cb2 |
| Optimism | 0xBC6f9d1CBa49DB365728478cefa02F6743617637 |
| Polygon | 0x007995f2AEcfBC745f20a7AE8D3a02c0EbF46264 |
| Unichain | 0xA7aBDb8f2108901c586543BD5e10E4fA263F4A47 |
=== "Testnet v1"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x0F78904c750801391EbBf308181e9d6fc892B0f3 |
| Solana Devnet | CXGRA5SCc8jxDbaQPZrmmZNu2JV34DP7gFW4m31uC1zs |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xc9c0A1030331D5dA0599D243eFd4682D906066D9 |
| Avalanche Fuji | 0x2cfEC91B50f657Cc86Ec693542527ac3e03bF742 |
| Aptos | 0x14a12d1fd6ef371b70c2113155534ec152ec7f779e281b54866c796c9a4a58d3? |
| Base Sepolia | 0x4983C6bD3bB7DA9EECe71cfa7AE4C67CAbf362F0 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x1F2e73E9AF5eecEdAF03b4F295f83BD587290867 |
=== "Mainnet v2"
| Ethereum | 0x2cCf230467FE7387674BAa657747F0B5485c7fEC |
| Solana | Supported |
| Arbitrum | 0x8442d68524217601ed126f6859694e4b0c7c66a1 |
| Avalanche | 0x3952914628650Ca510404872D84DfF10A844C5B5 |
| Base | 0xbd8d42f40a11b37bD1b3770D754f9629F7cd5679 |
| Codex | 0xE1Df8709CAa70c5eCEa0c27871cA7029Fcb0A0bd |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0xACD054f83c0b852d02503191e2c26527A7E72B1f |
| Ink | 0xD64341A38a5eAfb9EB9BACf8A5C52Fe858c4ABE9 |
| Linea | 0xc48c126468BE919068dE1983F00F65af759a4E87 |
| Optimism | 0xd0a8940b2e743e33b682daec4d52b46713606c9d |
| Plume | 0x486228859880ec6c05175035bEe2e5383D23B0fE |
| Polygon | 0xc8a8e6d760dcbd5d6746e2f66cd2ffa722dd1e59 |
| Seievm | 0xf4FefFc03EEFB06B009bFB168b60B30edf7abc12 |
| Sonic | 0xc39BF082ec91D9bC385F956D24a8D66C0c26223d |
| Unichain | 0xD5D5D640D8b758672Cc7A078734175c4433866d5 |
| World Chain | 0x789f2b91f7B35D5B890983328340c4600339B354 |
=== "Testnet v2"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x0F18DD26D0B41fb1eaa9cF34D1Ec6022aA69a8e2 |
| Solana Devnet | CXGRA5SCc8jxDbaQPZrmmZNu2JV34DP7gFW4m31uC1zs |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xC92946F22eA76bcB5Ee020525aC32d2098040570 |
| Avalanche Fuji | 0x4058F0C3924eDaB19c15597C438968ed49C1a213 |
| Base Sepolia | 0xC400FcC0e92d3406747FBb6f513D3aa8B038fcE9 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0xCCA1Cb361E3206faFcDBaCD99e02b32d730cf695 |
## NTT With Executor
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0xD2D9c936165a85F27a5a7e07aFb974D022B89463 |
| Solana | nex1gkSWtRBheEJuQZMqHhbMG5A45qPU76KqnCZNVHR |
| Arbitrum | 0x0Af42A597b0C201D4dcf450DcD0c06d55ddC1C77 |
| Avalanche | 0x4e9Af03fbf1aa2b79A2D4babD3e22e09f18Bb8EE |
| Base | 0x83216747fC21b86173D800E2960c0D5395de0F30 |
| Berachain | 0x0a2AF374Cc9CCCbB0Acc4E34B20b9d02a0f08c30 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x39B57Dd9908F8be02CfeE283b67eA1303Bc29fe1 |
| Celo | 0x3d69869fcB9e1CD1F4020b637fb8256030BAc8fC |
| CreditCoin | 0x5454b995719626256C96fb57454b044ffb3Da2F9 |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0x431017B1718b86898C7590fFcCC380DEf0456393 |
| Ink | 0x420370DC2ECC4D44b47514B7859fd11809BbeFF5 |
| Linea | 0xEAa5AddB5b8939Eb73F7faF46e193EefECaF13E9 |
| Mezo | 0x484b5593BbB90383f94FB299470F09427cf6cfE2 |
| Moonbeam | 0x1365593C8bae71a55e48E105a2Bb76d5928c7DE3 |
| Monad | 0x93FE94Ad887a1B04DBFf1f736bfcD1698D4cfF66Multi Ntt:0xFEA937F7124E19124671f1685671d3f04a9Af4E4 |
| Optimism | 0x85C0129bE5226C9F0Cf4e419D2fefc1c3FCa25cF |
| Plume | 0x6Eb53371f646788De6B4D0225a4Ed1d9267188AD |
| Polygon | 0x6762157b73941e36cEd0AEf54614DdE545d0F990 |
| Scroll | 0x055625d48968f99409244E8c3e03FbE73B235a62 |
| Seievm | 0x3F2D6441C7a59Dfe80f8e14142F9E28F6D440445 |
| Sonic | 0xaCa00703bb87F31D6F9fCcc963548b48FA46DfeB |
| Unichain | 0x607723D6353Dae3ef62B7B277Cfabd0F4bc6CB4C |
| World Chain | 0x66b1644400D51e104272337226De3EF1A820eC79 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x6bBd1ff3bB303F88835A714EE3241bF45DE26d29 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x54DD7080aE169DD923fE56d0C4f814a0a17B8f41 |
| Solana Devnet | nex1gkSWtRBheEJuQZMqHhbMG5A45qPU76KqnCZNVHR |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xd048170F1ECB8D47E499D3459aC379DA023E2C1B |
| Avalanche Fuji | 0x4e9Af03fbf1aa2b79A2D4babD3e22e09f18Bb8EE |
| Base Sepolia | 0x5845E08d890E21687F7Ebf7CbAbD360cD91c6245 |
| Celo | 0x3d69869fcB9e1CD1F4020b637fb8256030BAc8fC |
| Converge | 0x3d8c26b67BDf630FBB44F09266aFA735F1129197 |
| Fogo | nex1gkSWtRBheEJuQZMqHhbMG5A45qPU76KqnCZNVHR |
| Mezo | 0x484b5593BbB90383f94FB299470F09427cf6cfE2 |
| Monad | 0x93FE94Ad887a1B04DBFf1f736bfcD1698D4cfF66 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0xaDB1C56D363FF5A75260c3bd27dd7C1fC8421EF5 |
| Plume | 0x6Eb53371f646788De6B4D0225a4Ed1d9267188AD |
| Seievm | 0x3F2D6441C7a59Dfe80f8e14142F9E28F6D440445 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0xcDD9d7C759b29680f7a516d0058de8293b2AC7b1 |
## WTT Executor
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0xa8969F3f8D97b3Ed89D4e2EC19B6B0CfD504b212 |
| Solana | tbr7Qje6qBzPwfM52csL5KFi8ps5c5vDyiVVBLYVdRf |
| Arbitrum | 0x04C98824a64d75CD1E9Bc418088b4c9A99048153 |
| Avalanche | 0x8849F05675E034b54506caB84450c8C82694a786 |
| Base | 0xD8B736EF27Fc997b1d00F22FE37A58145D3BDA07 |
| Berachain | 0xFAeFa20CB3759AEd2310E25015F05d62D8567A3F |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x2513515340fF71DD5AF02fC1BdB9615704d91524 |
| Celo | 0xe478DEe705BEae591395B08934FA19F54df316BE |
| Fantom | 0xcafd2f0a35a4459fa40c0517e17e6fa2939441ca |
| Ink | 0x4bFB47F4c8A904d2C24e73601D175FE3a38aAb5B |
| Moonbeam | 0xF6b9616C63Fa48D07D82c93CE02B5d9111c51a3d |
| Optimism | 0x37aC29617AE74c750a1e4d55990296BAF9b8De73 |
| Polygon | 0x1d98CA4221516B9ac4869F5CeA7E6bb9C41609D6 |
| Scroll | 0x05129e142e7d5A518D81f19Db342fBF5f7E26A18 |
| Seievm | 0x7C129bc8F6188d12c0d1BBDE247F134148B97618 |
| Sui | 0x57f4e0ba41a7045e29d435bc66cc4175f381eb700e6ec16d4fdfe92e5a4dff9f |
| Unichain | 0x9Bca817F67f01557aeD615130825A28F4C5f3b87 |
| World Chain | 0xc0565Bd29b34603C0383598E16843d95Ae9c4f65 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x37bCc9d175124F77Bfce68589d2a8090eF846B85 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0xb0b2119067cF04fa959f654250BD49fE1BD6F53c |
| Solana | tbr7Qje6qBzPwfM52csL5KFi8ps5c5vDyiVVBLYVdRf |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xaE8dc4a7438801Ec4edC0B035EcCCcF3807F4CC1 |
| Avalanche | 0x10Ce9a35883C44640e8B12fea4Cc1e77F77D8c52 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x523d25D33B975ad72283f73B1103354352dBCBb8 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Celo | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Fantom | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Fogo | tbr7Qje6qBzPwfM52csL5KFi8ps5c5vDyiVVBLYVdRf |
| Mezo | 0x2002a44b1106DF83671Fb419A2079a75e2a34808 |
| Monad | 0x5Ba2c39cF0624BB5fBe94E919519aEA0DdD68454 |
| Moonbeam | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0xaE8dc4a7438801Ec4edC0B035EcCCcF3807F4CC1 |
| Sui | 0xb30040e5120f8cb853b691cb6d45981ae884b1d68521a9dc7c3ae881c0031923 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0xb00224c60fe6ab134c8544dc29350286545f8dcc |
## WTT Executor With Referrer
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Arbitrum | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Avalanche | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Base | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Berachain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Celo | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Ink | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Moonbeam | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Optimism | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Polygon | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Scroll | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Seievm | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Unichain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| World Chain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x13a35c075D6Acc1Fb9BddFE5FE38e7672789e4db |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Avalanche | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Mezo | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Monad | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x17CFAAf9e8a5ABb1eee758dB9040F945c9EAC907 |
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/messaging/reference/relayer-contract.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Relayer Contract
description: Reference for the Wormhole Relayer contract on EVM chains. Covers the proxy structure, components, state variables, functions, events, and errors.
categories: Reference
---
# Relayer Contract
The [Wormhole Relayer Contract on EVM](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayer.sol){target=\_blank} enables cross-chain message delivery with automatic execution on the destination chain. It publishes delivery instructions as Wormhole messages and defines the logic to process them via the `deliver` function. The contract supports optional value forwarding, gas refunds, message overrides, and integration with third-party delivery providers.
## Structure Overview
The Wormhole Relayer system on EVM is implemented as a modular, upgradeable contract suite, organized through layered inheritance and interfaces.
```text
IWormholeRelayer.sol (Interface)
└── WormholeRelayerBase.sol
├── WormholeRelayer.sol
├── CircleRelayer.sol
└── TypedUnits.sol
DeliveryProvider.sol (Standalone)
```
**Key Components:**
- **IWormholeRelayer.sol**: Defines the public interface for the Wormhole Relayer, including delivery functions and fee quoting.
- **WormholeRelayerBase.sol**: Base logic contract shared by both WormholeRelayer and CircleRelayer. Handles delivery processing, fee management, and VAA parsing.
- **WormholeRelayer.sol**: Main relayer implementation used with the Wormhole Messaging protocol. Inherits from `WormholeRelayerBase`.
- **CircleRelayer.sol**: Specialized implementation for Circle messages. Also extends `WormholeRelayerBase`, but is out of scope for this reference.
- **TypedUnits.sol**: Utility module for safe unit conversions, fee accounting, and delivery quote handling.
- **DeliveryProvider.sol**: Separate contract that sets and manages delivery pricing and supported chains. Queried by the relayer when calculating fees.
## State Variables
- **`chainId` ++"uint16"++**: Wormhole chain ID for the current network (e.g., 2 for Ethereum).
- **`wormhole` ++"IWormhole"++**: Address of the core Wormhole messaging contract used to verify VAAs.
- **`deliveryProvider` ++"address"++**: Address of the Delivery Provider contract responsible for quoting and setting delivery prices.
- **`rewardAddress` ++"address"++**: Address that receives excess fees collected from users.
- **`gasOverheads` ++"mapping(uint16 => GasOverhead)"++**: Per-chain gas overheads used to calculate delivery costs.
- **`supportedChains` ++"mapping(uint16 => bool)"++**: Tracks which destination chains are supported for message delivery.
- **`deliveries` ++"mapping(bytes32 => bool)"++**: Records completed deliveries (by VAA hash) to prevent replay.
- **`deliverySuccessBlock` ++"mapping(bytes32 => uint256)"++**: Stores the block number when a delivery succeeded (used for auditing).
- **`owner` ++"address"++**: Contract owner with permission to update system parameters (e.g., gas overheads).
- **`chainHash` ++"uint256"++**: EVM chain ID hash used for cross-checking delivery source chain.
- **`implementation` ++"address"++**: Address of the current logic contract (used in proxy pattern).
## Events
### SendEvent
Emitted when a send instruction is published and payment is handled. *(Defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event SendEvent(
uint64 indexed sequence,
LocalNative deliveryQuote,
LocalNative paymentForExtraReceiverValue
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the published delivery instruction message.
---
`deliveryQuote` ++"LocalNative"++
Price charged by the delivery provider (in source chain currency units).
---
`paymentForExtraReceiverValue` ++"LocalNative"++
Extra amount (in source chain currency units) used to top up the receiver value on the target chain.
### Delivery
Emitted after a delivery attempt is executed by a delivery provider. *(Defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event Delivery(
address indexed recipientContract,
uint16 indexed sourceChain,
uint64 indexed sequence,
bytes32 deliveryVaaHash,
DeliveryStatus status,
Gas gasUsed,
RefundStatus refundStatus,
bytes additionalStatusInfo,
bytes overridesInfo
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`recipientContract` ++"address"++
Target contract that was called.
---
`sourceChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID where the delivery was requested.
---
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the delivery VAA on the source chain.
---
`deliveryVaaHash` ++"bytes32"++
Hash of the delivery VAA.
---
`status` ++"DeliveryStatus"++
`SUCCESS` if the target call did not revert; `RECEIVER_FAILURE` if it reverted.
---
`gasUsed` ++"Gas"++
Gas consumed when calling the target contract.
---
`refundStatus` ++"RefundStatus"++
Result of the refund path (same-chain or cross-chain) or `NO_REFUND_REQUESTED`.
---
`additionalStatusInfo` ++"bytes"++
Empty on success; otherwise, truncated return data from the revert.
---
`overridesInfo` ++"bytes"++
Empty if not an override; otherwise, an encoded `DeliveryOverride`.
### ContractUpgraded (WormholeRelayer)
Emitted when the Wormhole Relayer contract is upgraded to a new implementation via governance. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event ContractUpgraded(
address indexed oldContract,
address indexed newContract
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`oldContract` ++"address"++
Address of the previous implementation.
---
`newContract` ++"address"++
Address of the new implementation.
### ContractUpgraded (DeliveryProvider)
Emitted when the Delivery Provider contract is upgraded to a new implementation. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event ContractUpgraded(
address indexed oldContract,
address indexed newContract
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`oldContract` ++"address"++
Address of the previous implementation.
---
`newContract` ++"address"++
Address of the new implementation.
### ChainSupportUpdated
Emitted when Delivery Provider support for a target chain is changed. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event ChainSupportUpdated(
uint16 targetChain,
bool isSupported
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID whose support setting changed.
---
`isSupported` ++"bool"++
Whether deliveries to `targetChain` are supported.
### OwnershipTransfered
Emitted when Delivery Provider ownership is transferred. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event OwnershipTransfered(
address indexed oldOwner,
address indexed newOwner
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`oldOwner` ++"address"++
Previous owner.
---
`newOwner` ++"address"++
New owner.
### RewardAddressUpdated
Emitted when the Delivery Provider reward address is updated. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event RewardAddressUpdated(
address indexed newAddress
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`newAddress` ++"address"++
New reward address.
### TargetChainAddressUpdated
Emitted when the Delivery Provider's peer address for a target chain is updated. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event TargetChainAddressUpdated(
uint16 indexed targetChain,
bytes32 indexed newAddress
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID whose peer address changed.
---
`newAddress` ++"bytes32"++
New peer address in Wormhole bytes32 format.
### DeliverGasOverheadUpdated
Emitted when the configured gas overhead for deliveries is updated. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event DeliverGasOverheadUpdated(
Gas indexed oldGasOverhead,
Gas indexed newGasOverhead
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`oldGasOverhead` ++"Gas"++
Previous overhead value.
---
`newGasOverhead` ++"Gas"++
New overhead value.
### WormholeRelayerUpdated
Emitted when the Delivery Provider's associated Wormhole Relayer address is updated. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event WormholeRelayerUpdated(
address coreRelayer
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`coreRelayer` ++"address"++
New Wormhole Relayer contract address on this chain.
### AssetConversionBufferUpdated
Emitted when the Delivery Provider's asset conversion buffer is updated. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
event AssetConversionBufferUpdated(
uint16 targetChain,
uint16 buffer,
uint16 bufferDenominator
);
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID whose buffer settings changed.
---
`buffer` ++"uint16"++
Buffer numerator.
---
`bufferDenominator` ++"uint16"++
Buffer denominator.
## Functions
### sendPayloadToEvm
Publishes an instruction for the default delivery provider to relay a payload to an EVM target. Must be called with `msg.value == quoteEVMDeliveryPrice(targetChain, receiverValue, gasLimit)`. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function sendPayloadToEvm(
uint16 targetChain,
address targetAddress,
bytes memory payload,
TargetNative receiverValue,
Gas gasLimit
) external payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`targetAddress` ++"address"++
Contract on the destination chain (must implement `IWormholeReceiver`).
---
`payload` ++"bytes"++
Bytes delivered to `targetAddress`.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Value (destination chain Wei) to forward to `targetAddress`.
---
`gasLimit` ++"Gas"++
Gas limit for calling `targetAddress`.
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the published delivery instruction.
### sendPayloadToEvm (with refund)
Same as above, but sends any refund to refundAddress on refundChain. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function sendPayloadToEvm(
uint16 targetChain,
address targetAddress,
bytes memory payload,
TargetNative receiverValue,
Gas gasLimit,
uint16 refundChain,
address refundAddress
) external payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`targetAddress` ++"address"++
Contract on the destination chain (must implement `IWormholeReceiver`).
---
`payload` ++"bytes"++
Bytes delivered to `targetAddress`.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Value (destination chain Wei) to forward to `targetAddress`.
---
`gasLimit` ++"Gas"++
Gas limit for calling `targetAddress`.
---
`refundChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID where refunds should be sent.
---
`refundAddress` ++"address"++
Address on `refundChain` to receive refunds.
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the published delivery instruction.
### sendVaasToEvm (with refund)
Publishes an instruction (default delivery provider) to relay a payload and additional VAAs. Refunds go to `refundAddress` on `refundChain`. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function sendVaasToEvm(
uint16 targetChain,
address targetAddress,
bytes memory payload,
TargetNative receiverValue,
Gas gasLimit,
VaaKey[] memory vaaKeys,
uint16 refundChain,
address refundAddress
) external payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`targetAddress` ++"address"++
Contract on the destination chain (must implement `IWormholeReceiver`).
---
`payload` ++"bytes"++
Bytes delivered to `targetAddress`.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Value (destination chain Wei) to forward to `targetAddress`.
---
`gasLimit` ++"Gas"++
Gas limit for calling `targetAddress`.
---
`vaaKeys` ++"VaaKey[]"++
Extra Wormhole messages (VAAs) to deliver along with `payload`.
---
`refundChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID where any refund will be sent.
---
`refundAddress` ++"address"++
Address on `refundChain` that receives any refund.
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the published delivery instruction.
### sendToEvm (MessageKeys)
Publishes an instruction using a specific delivery provider, optionally attaching extra receiver value funded on the source chain and arbitrary MessageKeys (e.g., VAAs or other supported keys). *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function sendToEvm(
uint16 targetChain,
address targetAddress,
bytes memory payload,
TargetNative receiverValue,
LocalNative paymentForExtraReceiverValue,
Gas gasLimit,
uint16 refundChain,
address refundAddress,
address deliveryProviderAddress,
MessageKey[] memory messageKeys,
uint8 consistencyLevel
) external payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`targetAddress` ++"address"++
Contract on the destination chain (must implement `IWormholeReceiver`).
---
`payload` ++"bytes"++
Bytes delivered to `targetAddress`.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Value (destination chain Wei) to forward to `targetAddress`.
---
`paymentForExtraReceiverValue` ++"LocalNative"++
Extra source chain amount. The delivery provider converts this to destination native and adds it to `receiverValue`.
---
`gasLimit` ++"Gas"++
Gas limit for calling `targetAddress` on the destination chain.
---
`refundChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID where any refund will be sent.
---
`refundAddress` ++"address"++
Address on `refundChain` that receives any refund.
---
`deliveryProviderAddress` ++"address"++
Chosen delivery provider (must implement `IDeliveryProvider`).
---
`messageKeys` ++"MessageKey[]"++
External messages to deliver (e.g., VAAs). Each key’s `keyType` **must** be supported by the delivery provider; otherwise the call reverts.
---
`consistencyLevel` ++"uint8"++
Wormhole publishing consistency (e.g., instant vs. finalized) used when emitting the delivery instruction.
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the published delivery instruction.
### send (MessageKeys, generic)
Generic chain-agnostic form (addresses are Wormhole-formatted bytes32, and execution params are encoded). *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function send(
uint16 targetChain,
bytes32 targetAddress,
bytes memory payload,
TargetNative receiverValue,
LocalNative paymentForExtraReceiverValue,
bytes memory encodedExecutionParameters,
uint16 refundChain,
bytes32 refundAddress,
address deliveryProviderAddress,
MessageKey[] memory messageKeys,
uint8 consistencyLevel
) external payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`targetAddress` ++"bytes32"++
Wormhole-formatted 32-byte address of the destination contract.
---
`payload` ++"bytes"++
Bytes delivered to `targetAddress`.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Amount of destination chain native (e.g., Wei) forwarded to `targetAddress`.
---
`paymentForExtraReceiverValue` ++"LocalNative"++
Extra source chain native to be converted by the delivery provider and added to `receiverValue`.
---
`encodedExecutionParameters` ++"bytes"++
Versioned execution params for the target chain (e.g., for EVM use `encodeEvmExecutionParamsV1(EvmExecutionParamsV1(gasLimit))`).
---
`refundChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID where any refund will be sent.
---
`refundAddress` ++"bytes32"++
Wormhole-formatted address on `refundChain` that receives any refund.
---
`deliveryProviderAddress` ++"address"++
Chosen delivery provider (must implement `IDeliveryProvider`).
---
`messageKeys` ++"MessageKey[]"++
External messages to deliver (e.g., VAAs). Each key’s `keyType` **must** be supported by the delivery provider.
---
`consistencyLevel` ++"uint8"++
Wormhole publishing consistency used when emitting the delivery instruction.
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the published delivery instruction.
### resendToEvm
Requests a previously published delivery instruction to be redelivered (EVM convenience). *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function resendToEvm(
VaaKey memory deliveryVaaKey,
uint16 targetChain,
TargetNative newReceiverValue,
Gas newGasLimit,
address newDeliveryProviderAddress
) external payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`deliveryVaaKey` ++"VaaKey"++
Identifies the original delivery instruction VAA.
---
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID where the message should be redelivered.
---
`newReceiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Updated value sent to the target contract.
---
`newGasLimit` ++"Gas"++
Updated gas limit for the target call.
---
`newDeliveryProviderAddress` ++"address"++
Delivery provider to use for the redelivery.
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the redelivery instruction.
### resend (generic)
Generic redelivery (chain-agnostic execution params). *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function resend(
VaaKey memory deliveryVaaKey,
uint16 targetChain,
TargetNative newReceiverValue,
bytes memory newEncodedExecutionParameters,
address newDeliveryProviderAddress
) external payable returns (uint64 sequence)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`deliveryVaaKey` ++"VaaKey"++
Identifies the original delivery instruction VAA.
---
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID where the message should be redelivered.
---
`newReceiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Updated value to forward to the target contract on the destination chain.
---
`newEncodedExecutionParameters` ++"bytes"++
Versioned, chain-specific execution params for the redelivery (e.g., for EVM use `encodeEvmExecutionParamsV1(EvmExecutionParamsV1(gasLimit))`).
---
`newDeliveryProviderAddress` ++"address"++
Delivery provider to use for the redelivery (must implement `IDeliveryProvider`).
??? interface "Returns"
`sequence` ++"uint64"++
Sequence number of the redelivery instruction.
### quoteEVMDeliveryPrice (default provider)
Returns the price and refund-per-gas info for an EVM delivery using the default provider. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function quoteEVMDeliveryPrice(
uint16 targetChain,
TargetNative receiverValue,
Gas gasLimit
) external view returns (LocalNative nativePriceQuote, GasPrice targetChainRefundPerGasUnused)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Amount of destination chain Wei that will be forwarded to the target contract.
---
`gasLimit` ++"Gas"++
Gas limit that will be used to call the target contract.
??? interface "Returns"
`nativePriceQuote` ++"LocalNative"++
Source chain price to request the delivery.
---
`targetChainRefundPerGasUnused` ++"GasPrice"++
Refund rate per unused gas on target chain.
### quoteEVMDeliveryPrice (explicit provider)
Same as above, but quotes using a given provider. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function quoteEVMDeliveryPrice(
uint16 targetChain,
TargetNative receiverValue,
Gas gasLimit,
address deliveryProviderAddress
) external view returns (LocalNative nativePriceQuote, GasPrice targetChainRefundPerGasUnused)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Amount of destination chain Wei to forward to the target contract.
---
`gasLimit` ++"Gas"++
Gas limit to call the target contract with.
---
`deliveryProviderAddress` ++"address"++
Address of the chosen provider (implements `IDeliveryProvider`).
??? interface "Returns"
`nativePriceQuote` ++"LocalNative"++
Source chain price to request this delivery.
---
`targetChainRefundPerGasUnused` ++"GasPrice"++
Refund rate per unit of unused gas on the destination chain.
### quoteDeliveryPrice (generic)
Generic quote (versioned execution params), returning price and provider's encoded execution info. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function quoteDeliveryPrice(
uint16 targetChain,
TargetNative receiverValue,
bytes memory encodedExecutionParameters,
address deliveryProviderAddress
) external view returns (LocalNative nativePriceQuote, bytes memory encodedExecutionInfo)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`receiverValue` ++"TargetNative"++
Amount of destination chain Wei to forward to the target contract.
---
`encodedExecutionParameters` ++"bytes"++
Versioned execution parameters (e.g., for `EVM_V1`, encodes the gas limit).
---
`deliveryProviderAddress` ++"address"++
Address of the chosen provider (implements `IDeliveryProvider`).
??? interface "Returns"
`nativePriceQuote` ++"LocalNative"++
Source chain price to request this delivery.
---
`encodedExecutionInfo` ++"bytes"++
Provider's encoded execution info (e.g., for `EVM_V1`, includes gas limit and refund-per-gas).
### quoteNativeForChain
Converts a source chain amount into extra value that will be delivered on the target chain. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function quoteNativeForChain(
uint16 targetChain,
LocalNative currentChainAmount,
address deliveryProviderAddress
) external view returns (TargetNative targetChainAmount)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`targetChain` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID of the destination chain.
---
`currentChainAmount` ++"LocalNative"++
Amount paid on the source chain to fund extra receiver value.
---
`deliveryProviderAddress` ++"address"++
Address of the chosen provider (implements `IDeliveryProvider`).
??? interface "Returns"
`targetChainAmount` ++"TargetNative"++
Extra destination chain Wei that will be added to the call's value.
### getDefaultDeliveryProvider
Returns the current default delivery provider address. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerSend.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerSend.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function getDefaultDeliveryProvider() external view returns (address deliveryProvider)
```
??? interface "Returns"
`deliveryProvider` ++"address"++
Address of the default `IDeliveryProvider` on this chain.
### deliver
Called by a delivery provider to execute a delivery on the target chain. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function deliver(
bytes[] memory encodedVMs,
bytes memory encodedDeliveryVAA,
address payable relayerRefundAddress,
bytes memory deliveryOverrides
) external payable
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`encodedVMs` ++"bytes[]"+
Signed Wormhole messages to relay.
---
`encodedDeliveryVAA` ++"bytes"++
Signed WormholeRelayer instruction VAA.
---
`relayerRefundAddress` ++"address payable"++
Address to receive any relayer refund.
---
`deliveryOverrides` ++"bytes"++
Optional encoded overrides (or empty).
### deliveryAttempted
Checks whether a delivery attempt has been made for a given hash. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerBase.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerBase.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function deliveryAttempted(bytes32 deliveryHash) external view returns (bool attempted)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`deliveryHash` ++"bytes32"++
Hash of the delivery VAA.
??? interface "Returns"
`attempted` ++"bool"++
`true` if a success or failure block was recorded for this hash.
### deliverySuccessBlock
Block number when a delivery was successfully executed. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerBase.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerBase.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function deliverySuccessBlock(bytes32 deliveryHash) external view returns (uint256 blockNumber)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`deliveryHash` ++"bytes32"++
Hash of the delivery VAA.
??? interface "Returns"
`blockNumber` ++"uint256"++
Block number where the delivery was marked successful (0 if never successful).
### deliveryFailureBlock
Block number of the latest failed delivery attempt. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerBase.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerBase.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function deliveryFailureBlock(bytes32 deliveryHash) external view returns (uint256 blockNumber)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`deliveryHash` ++"bytes32"++
Hash of the delivery VAA.
??? interface "Returns"
`blockNumber` ++"uint256"++
Block number of the most recent failed attempt (0 if none).
### getRegisteredWormholeRelayerContract
Returns the registered Wormhole Relayer contract address (wormhole format) for a given chain ID. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerBase.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerBase.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function getRegisteredWormholeRelayerContract(uint16 chainId) external view returns (bytes32)
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`chainId` ++"uint16"++
Wormhole chain ID.
??? interface "Returns"
`address` ++"bytes32"++
Wormhole-formatted address of the relayer contract registered for `chainId` (zero if none).
### registerWormholeRelayerContract
Registers a Wormhole Relayer contract deployed on another chain (governance VM required). *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function registerWormholeRelayerContract(bytes memory encodedVm) external
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`encodedVm` ++"bytes"++
Signed governance VM that encodes the `foreignChainId` and `foreignContractAddress`.
### setDefaultDeliveryProvider
Sets the default delivery provider via a governance VM. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function setDefaultDeliveryProvider(bytes memory encodedVm) external
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`encodedVm` ++"bytes"++
Signed governance VM that encodes the new provider address.
### submitContractUpgrade
Upgrades the Wormhole Relayer contract to a new implementation (governance VM required). *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
```solidity
function submitContractUpgrade(bytes memory encodedVm) external
```
??? interface "Parameters"
`encodedVm` ++"bytes"++
Signed governance VM that encodes the new implementation address.
## Errors
### InvalidDeliveryVaa
Thrown when the delivery VAA fails `parseAndVerifyVM`. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidEmitter
Emitted when the VAA emitter is not the registered Wormhole Relayer for the source chain. *(Used in WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### InsufficientRelayerFunds
Reverts if `msg.value` is less than the required execution + refund budget on the target chain. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### TargetChainIsNotThisChain
Reverts when the instruction's `targetChain` does not match the current chain. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### MessageKeysLengthDoesNotMatchMessagesLength
Reverts when the provided message keys do not match the number of delivered messages. (Used in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank}), defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})
### VaaKeysDoNotMatchVaas
Reverts when described VAAs don't match the actual VAAs delivered. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidOverrideGasLimit
Reverts if a redelivery override sets a gas limit lower than the original. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidOverrideReceiverValue
Reverts if a redelivery override sets a receiver value lower than the original. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### InvalidMsgValue
Reverts when msg.value does not equal `wormholeMessageFee` + `deliveryQuote` + `paymentForExtraReceiverValue`. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerBase.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerBase.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### ReentrantDelivery
Reverts on re-entrant calls to relayer entrypoints guarded by `nonReentrant`. *(Used in [WormholeRelayerBase.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerBase.sol){target=\_blank}, defined in [IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/interfaces/relayer/IWormholeRelayerTyped.sol){target=\_blank})*
### CallerNotApproved(address msgSender)
Custom error declared for access checks. *(Defined in [DeliveryProvider.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProvider.sol){target=\_blank})*
### PriceIsZero(uint16 chain)
Reverts if a required price value for a chain is zero during quoting/conversion. *(Defined in [DeliveryProvider.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProvider.sol){target=\_blank})*
### Overflow(uint256 value, uint256 max)
Reverts when an internal quote exceeds a type's allowed maximum (e.g., gas overhead/price bounds). *(Defined in [DeliveryProvider.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProvider.sol){target=\_blank})*
### MaxRefundGreaterThanGasLimitCost(uint256 maxRefund, uint256 gasLimitCost)
Declared to guard refund limits vs. gas limit cost. *(Defined in [DeliveryProvider.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProvider.sol){target=\_blank})*
### MaxRefundGreaterThanGasLimitCostOnSourceChain(uint256 maxRefund, uint256 gasLimitCost)
Declared to guard source chain refund limits vs. gas limit cost. *(Defined in [DeliveryProvider.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProvider.sol){target=\_blank})*
### ExceedsMaximumBudget(uint16 targetChain, uint256 exceedingValue, uint256 maximumBudget)
Reverts when required target-chain Wei (receiver value + gas) exceeds that chain's configured maximum budget. *(Defined in [DeliveryProvider.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProvider.sol){target=\_blank})*
### ChainIdIsZero()
Reverts if an update is attempted with `chainId = 0`. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### GasPriceIsZero()
Reverts if a price update sets gas price to zero. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### NativeCurrencyPriceIsZero()
Reverts if a price update sets native currency price to zero. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### FailedToInitializeImplementation(string reason)
Reverts if the implementation's `initialize()` delegatecall fails during upgrade/setup. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank} and [DeliveryProviderSetup.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderSetup.sol){target=\_blank})*
### WrongChainId()
Reverts when an operation is invoked with a chainId that doesn't match the contract's configured chain. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### AddressIsZero()
Reverts if a zero address is provided where a nonzero address is required (e.g., ownership handoff). *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### CallerMustBePendingOwner()
Reverts if `confirmOwnershipTransferRequest` is called by an address other than `pendingOwner`. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### CallerMustBeOwner()
Reverts on functions guarded by `onlyOwner` when `msg.sender` is not the owner. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### CallerMustBeOwnerOrPricingWallet()
Reverts on functions guarded by `onlyOwnerOrPricingWallet` when caller is neither. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderGovernance.sol){target=\_blank})*
### ImplementationAlreadyInitialized()
Reverts if `initialize()` is called on an implementation that was already initialized. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderImplementation.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderImplementation.sol){target=\_blank})*
### ImplementationAddressIsZero()
Reverts if `setup()` is called with a zero implementation address. *(Defined in [DeliveryProviderSetup.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/deliveryProvider/DeliveryProviderSetup.sol){target=\_blank})*
### UnexpectedExecutionInfoVersion
Reverts when the `executionInfoVersion` in the delivery VAA does not match the expected version. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank})*
### VersionMismatchOverride
Reverts when the override's `executionInfoVersion` does not match the original delivery's version. *(Defined in [WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/relayer/ethereum/contracts/relayer/wormholeRelayer/WormholeRelayerDelivery.sol){target=\_blank})*
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/chain-ids.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Chain IDs
description: This page documents the Wormhole-specific chain IDs for each chain and contrasts them to the more commonly referenced EVM chain IDs originating in EIP-155.
categories: Reference
---
# Chain IDs
The following table documents the chain IDs used by Wormhole and places them alongside the more commonly referenced [EVM Chain IDs](https://chainlist.org/){target=\_blank}.
!!! note
Please note, Wormhole chain IDs are different than the more commonly referenced [EVM chain IDs](https://chainlist.org/){target=\_blank}, specified in the Mainnet and Testnet ID columns.
!!!warning
Wormhole Contributors recommend that all connected chains implement robust security practices including (but not exclusively): open sourcing code and running public bug bounty programs, undergoing security audits and publishing those reports, using version control with adequate access controls and mandatory code review, and high unit and integration test coverage where the results of those tests are available publicly. Connected chains that can't verifiably prove that they've implemented a high percentage of these practices may be noted below with the :warning: symbol.
Wormhole integrators are encouraged to understand the security assumptions of any chain before trusting messages from it. See the recommended security practices for chains in [Wormhole's security program](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole/blob/main/SECURITY.md#chain-integrators){target=\_blank}.
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 2 | 1 |
| Solana | 1 | Mainnet Beta-5eykt4UsFv8P8NJdTREpY1vzqKqZKvdpKuc147dw2N9d |
| Algorand | 8 | mainnet-v1.0 |
| Aptos | 22 | 1 |
| Arbitrum | 23 | Arbitrum One-42161 |
| Avalanche | 6 | C-Chain-43114 |
| Base | 30 | Base-8453 |
| Berachain | 39 | |
| BNB Smart Chain | 4 | 56 |
| Celestia | 4004 | celestia |
| Celo | 14 | 42220 |
| Converge | 53 | |
| Cosmos Hub | 4000 | cosmoshub-4 |
| CreditCoin | 59 | |
| Dymension | 4007 | dymension_1100-1 |
| Evmos | 4001 | evmos_9001-2 |
| Fantom | 10 | 250 |
| Fogo | 51 | |
| HyperCore | 65000 | 20000 |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 47 | |
| Injective | 19 | injective-1 |
| Ink | 46 | |
| Kaia | 13 | 8217 |
| Kujira | 4002 | kaiyo-1 |
| Linea | 38 | 59144 |
| Mantle | 35 | 5000 |
| Mezo | 50 | |
| Monad | 48 | |
| Moonbeam | 16 | 1284 |
| NEAR | 15 | mainnet |
| Neutron | 4003 | neutron-1 |
| Noble | 4009 | noble-1 |
| Optimism | 24 | 10 |
| Osmosis | 20 | osmosis-1 |
| Plasma | 58 | |
| Plume | 55 | 98866 |
| Polygon | 5 | 137 |
| Provenance | 4008 | pio-mainnet-1 |
| Pythnet | 26 | |
| Scroll | 34 | 534352 |
| SEDA | 4006 | |
| Sei | 32 | pacific-1 |
| Seievm | 40 | |
| Sonic | 52 | 146 |
| Stacks | 60 | 1 |
| Stargaze | 4005 | stargaze-1 |
| Sui | 21 | 35834a8a |
| Unichain | 44 | |
| World Chain | 45 | 480 |
| X Layer | 37 | 196 |
| XRPL-EVM | 57 | 1440000 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Holesky | 10006 | Holesky-17000 |
| Ethereum Sepolia | 10002 | Sepolia-11155111 |
| Solana | 1 | Devnet-EtWTRABZaYq6iMfeYKouRu166VU2xqa1wcaWoxPkrZBG |
| Algorand | 8 | testnet-v1.0 |
| Aptos | 22 | 2 |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 10003 | Sepolia-421614 |
| Avalanche | 6 | Fuji-43113 |
| Base Sepolia | 10004 | Base Sepolia-84532 |
| Berachain | 39 | 80084 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 4 | 97 |
| Celestia | 4004 | mocha-4 |
| Celo | 14 | Alfajores-44787 |
| Converge | 53 | 52085145 |
| Cosmos Hub | 4000 | theta-testnet-001 |
| CreditCoin | 59 | |
| Dymension | 4007 | |
| Evmos | 4001 | evmos_9000-4 |
| Fantom | 10 | 4002 |
| Fogo | 51 | 9GGSFo95raqzZxWqKM5tGYvJp5iv4Dm565S4r8h5PEu9 |
| HyperCore | 65000 | 20000 |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 47 | 998 |
| Injective | 19 | injective-888 |
| Ink | 46 | 763373 |
| Kaia | 13 | Kairos-1001 |
| Kujira | 4002 | harpoon-4 |
| Linea | 38 | 59141 |
| Mantle | 35 | Sepolia-5003 |
| Mezo | 50 | 31611 |
| Monad | 48 | 10143 |
| Moonbeam | 16 | Moonbase-Alphanet-1287 |
| NEAR | 15 | testnet |
| Neutron | 4003 | pion-1 |
| Noble | 4009 | grand-1 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 10005 | Optimism Sepolia-11155420 |
| Osmosis | 20 | osmo-test-5 |
| Plasma | 58 | |
| Plume | 55 | 98867 |
| Polygon Amoy | 10007 | Amoy-80002 |
| Provenance | 4008 | |
| Pythnet | 26 | |
| Scroll | 34 | Sepolia-534351 |
| SEDA | 4006 | seda-1-testnet |
| Sei | 32 | atlantic-2 |
| Seievm | 40 | |
| Sonic | 52 | 57054 |
| Stargaze | 4005 | |
| Sui | 21 | 4c78adac |
| Unichain | 44 | Unichain Sepolia-1301 |
| World Chain | 45 | 4801 |
| X Layer | 37 | 195 |
| XRPL-EVM | 57 | 1449000 |
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/consistency-levels.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Wormhole Finality | Consistency Levels
description: This page documents how long to wait for finality before signing, based on each chain’s consistency (finality) level and consensus mechanism.
categories: Reference
---
# Wormhole Finality
The following table documents each chain's `consistencyLevel` values (i.e., finality reached before signing). The consistency level defines how long the Guardians should wait before signing a VAA. The finalization time depends on the specific chain's consensus mechanism. The consistency level is a `u8`, so any single byte may be used. However, a small subset has particular meanings. If the `consistencyLevel` isn't one of those specific values, the `Otherwise` column describes how it's interpreted.
| Ethereum | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 19min | Details |
| Solana | | 0 | 1 | | ~ 14s | Details |
| Algorand | | | 0 | | ~ 4s | Details |
| Aptos | | | 0 | | ~ 4s | Details |
| Arbitrum | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 18min | Details |
| Avalanche | 200 | | | finalized | ~ 2s | Details |
| Base | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 18min | |
| Berachain | 200 | | | finalized | ~ 4s | |
| BNB Smart Chain | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 48s | Details |
| Celestia | | | 0 | | ~ 5s | |
| Celo | 200 | | | finalized | ~ 10s | |
| Converge | | | 0 | | ~ 7min | |
| Cosmos Hub | | | 0 | | ~ 5s | |
| CreditCoin | | | 0 | | ~ 60s | |
| Dymension | | | 0 | | ~ 5s | |
| Evmos | | | 0 | | ~ 2s | |
| Fantom | 200 | | | finalized | ~ 5s | |
| Fogo | | | 0 | | ~ 14s | |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | | | 0 | | ~ 2s | |
| Injective | | | 0 | | ~ 3s | |
| Ink | | | 0 | | ~ 9min | |
| Kaia | 200 | | | finalized | ~ 1s | |
| Kujira | | | 0 | | ~ 3s | |
| Mantle | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 18min | |
| Mezo | | | 0 | | ~ 8s | |
| Monad | | | 0 | | ~ 2s | |
| Moonbeam | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 24s | Details |
| NEAR | | | 0 | | ~ 2s | Details |
| Neutron | | | 0 | | ~ 5s | |
| Optimism | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 18min | |
| Osmosis | | | 0 | | ~ 6s | |
| Plasma | | | 0 | | ~ 3s | |
| Plume | | | 0 | | ~ 18min | |
| Polygon | 200 | | | finalized | ~ 66s | Details |
| Scroll | 200 | | | finalized | ~ 16min | |
| Sei | | | 0 | | ~ 1s | |
| Seievm | | | 0 | | ~ 1s | |
| Sonic | | | 0 | | ~ 1s | |
| Stacks | | | 0 | | ~ 61min | |
| Stargaze | | | 0 | | ~ 5s | |
| Sui | | | 0 | | ~ 3s | Details |
| Unichain | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 18min | |
| World Chain | | | 0 | | ~ 18min | |
| X Layer | 200 | 201 | | finalized | ~ 16min | |
| XRPL-EVM | | | 0 | | ~ 10s | |
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/contract-addresses.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Contract Addresses
description: This page documents the deployed contract addresses of the Wormhole contracts on each chain, including Core Contracts, TokenBridge, and more.
categories: Reference
---
# Contract Addresses
## Core Contracts
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x98f3c9e6E3fAce36bAAd05FE09d375Ef1464288B |
| Solana | worm2ZoG2kUd4vFXhvjh93UUH596ayRfgQ2MgjNMTth |
| Algorand | 842125965 |
| Aptos | 0x5bc11445584a763c1fa7ed39081f1b920954da14e04b32440cba863d03e19625 |
| Arbitrum | 0xa5f208e072434bC67592E4C49C1B991BA79BCA46 |
| Avalanche | 0x54a8e5f9c4CbA08F9943965859F6c34eAF03E26c |
| Base | 0xbebdb6C8ddC678FfA9f8748f85C815C556Dd8ac6 |
| Berachain | 0xCa1D5a146B03f6303baF59e5AD5615ae0b9d146D |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x98f3c9e6E3fAce36bAAd05FE09d375Ef1464288B |
| Celo | 0xa321448d90d4e5b0A732867c18eA198e75CAC48E |
| CreditCoin | 0xaBf89de706B583424328B54dD05a8fC986750Da8 |
| Fantom | 0x126783A6Cb203a3E35344528B26ca3a0489a1485 |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0x7C0faFc4384551f063e05aee704ab943b8B53aB3 |
| Injective | inj17p9rzwnnfxcjp32un9ug7yhhzgtkhvl9l2q74d |
| Ink | 0xCa1D5a146B03f6303baF59e5AD5615ae0b9d146D |
| Kaia | 0x0C21603c4f3a6387e241c0091A7EA39E43E90bb7 |
| Linea | 0x0C56aebD76E6D9e4a1Ec5e94F4162B4CBbf77b32 |
| Mantle | 0xbebdb6C8ddC678FfA9f8748f85C815C556Dd8ac6 |
| Mezo | 0xaBf89de706B583424328B54dD05a8fC986750Da8 |
| Moonbeam | 0xC8e2b0cD52Cf01b0Ce87d389Daa3d414d4cE29f3 |
| NEAR | contract.wormhole_crypto.near |
| Neutron | neutron16rerygcpahqcxx5t8vjla46ym8ccn7xz7rtc6ju5ujcd36cmc7zs9zrunh |
| Optimism | 0xEe91C335eab126dF5fDB3797EA9d6aD93aeC9722 |
| Plume | 0xaBf89de706B583424328B54dD05a8fC986750Da8 |
| Polygon | 0x7A4B5a56256163F07b2C80A7cA55aBE66c4ec4d7 |
| Pythnet | H3fxXJ86ADW2PNuDDmZJg6mzTtPxkYCpNuQUTgmJ7AjU |
| Scroll | 0xbebdb6C8ddC678FfA9f8748f85C815C556Dd8ac6 |
| Sei | sei1gjrrme22cyha4ht2xapn3f08zzw6z3d4uxx6fyy9zd5dyr3yxgzqqncdqn |
| Seievm | 0xCa1D5a146B03f6303baF59e5AD5615ae0b9d146D |
| Sui | 0xaeab97f96cf9877fee2883315d459552b2b921edc16d7ceac6eab944dd88919c |
| Unichain | 0xCa1D5a146B03f6303baF59e5AD5615ae0b9d146D |
| World Chain | 0xcbcEe4e081464A15d8Ad5f58BB493954421eB506 |
| X Layer | 0x194B123c5E96B9b2E49763619985790Dc241CAC0 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0xaBf89de706B583424328B54dD05a8fC986750Da8 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Holesky | 0xa10f2eF61dE1f19f586ab8B6F2EbA89bACE63F7a |
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x4a8bc80Ed5a4067f1CCf107057b8270E0cC11A78 |
| Solana | 3u8hJUVTA4jH1wYAyUur7FFZVQ8H635K3tSHHF4ssjQ5 |
| Algorand | 86525623 |
| Aptos | 0x5bc11445584a763c1fa7ed39081f1b920954da14e04b32440cba863d03e19625 |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0x6b9C8671cdDC8dEab9c719bB87cBd3e782bA6a35 |
| Avalanche | 0x7bbcE28e64B3F8b84d876Ab298393c38ad7aac4C |
| Base Sepolia | 0x79A1027a6A159502049F10906D333EC57E95F083 |
| Berachain | 0xBB73cB66C26740F31d1FabDC6b7A46a038A300dd |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x68605AD7b15c732a30b1BbC62BE8F2A509D74b4D |
| Celo | 0x88505117CA88e7dd2eC6EA1E13f0948db2D50D56 |
| Converge | 0x556B259cFaCd9896B2773310080c7c3bcE90Ff01 |
| CreditCoin | 0xaBf89de706B583424328B54dD05a8fC986750Da8 |
| Fantom | 0x1BB3B4119b7BA9dfad76B0545fb3F531383c3bB7 |
| Fogo | BhnQyKoQQgpuRTRo6D8Emz93PvXCYfVgHhnrR4T3qhw4 |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0xBB73cB66C26740F31d1FabDC6b7A46a038A300dd |
| Injective | inj1xx3aupmgv3ce537c0yce8zzd3sz567syuyedpg |
| Ink | 0xBB73cB66C26740F31d1FabDC6b7A46a038A300dd |
| Kaia | 0x1830CC6eE66c84D2F177B94D544967c774E624cA |
| Linea | 0x79A1027a6A159502049F10906D333EC57E95F083 |
| Mantle | 0x376428e7f26D5867e69201b275553C45B09EE090 |
| Mezo | 0x268557122Ffd64c85750d630b716471118F323c8 |
| Monad | 0xBB73cB66C26740F31d1FabDC6b7A46a038A300dd |
| Moonbeam | 0xa5B7D85a8f27dd7907dc8FdC21FA5657D5E2F901 |
| NEAR | wormhole.wormhole.testnet |
| Neutron | neutron1enf63k37nnv9cugggpm06mg70emcnxgj9p64v2s8yx7a2yhhzk2q6xesk4 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x31377888146f3253211EFEf5c676D41ECe7D58Fe |
| Osmosis | osmo1hggkxr0hpw83f8vuft7ruvmmamsxmwk2hzz6nytdkzyup9krt0dq27sgyx |
| Plasma | 0xaBf89de706B583424328B54dD05a8fC986750Da8 |
| Plume | 0x81705b969cDcc6FbFde91a0C6777bE0EF3A75855 |
| Polygon Amoy | 0x6b9C8671cdDC8dEab9c719bB87cBd3e782bA6a35 |
| Pythnet | EUrRARh92Cdc54xrDn6qzaqjA77NRrCcfbr8kPwoTL4z |
| Scroll | 0x055F47F1250012C6B20c436570a76e52c17Af2D5 |
| Sei | sei1nna9mzp274djrgzhzkac2gvm3j27l402s4xzr08chq57pjsupqnqaj0d5s |
| Seievm | 0xBB73cB66C26740F31d1FabDC6b7A46a038A300dd |
| Sui | 0x31358d198147da50db32eda2562951d53973a0c0ad5ed738e9b17d88b213d790 |
| Unichain | 0xBB73cB66C26740F31d1FabDC6b7A46a038A300dd |
| World Chain | 0xe5E02cD12B6FcA153b0d7fF4bF55730AE7B3C93A |
| X Layer | 0xA31aa3FDb7aF7Db93d18DDA4e19F811342EDF780 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0xaBf89de706B583424328B54dD05a8fC986750Da8 |
=== "Devnet"
| Ethereum | 0xC89Ce4735882C9F0f0FE26686c53074E09B0D550 |
| Solana | Bridge1p5gheXUvJ6jGWGeCsgPKgnE3YgdGKRVCMY9o |
| Algorand | 1004 |
| Aptos | 0xde0036a9600559e295d5f6802ef6f3f802f510366e0c23912b0655d972166017 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0xC89Ce4735882C9F0f0FE26686c53074E09B0D550 |
| NEAR | wormhole.test.near |
| Stacks | ST1PQHQKV0RJXZFY1DGX8MNSNYVE3VGZJSRTPGZGM |
| Sui | 0x5a5160ca3c2037f4b4051344096ef7a48ebf4400b3f385e57ea90e1628a8bde0 |
## Wrapped Token Transfers (WTT)
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x3ee18B2214AFF97000D974cf647E7C347E8fa585 |
| Solana | wormDTUJ6AWPNvk59vGQbDvGJmqbDTdgWgAqcLBCgUb |
| Algorand | 842126029 |
| Aptos | 0x576410486a2da45eee6c949c995670112ddf2fbeedab20350d506328eefc9d4f |
| Arbitrum | 0x0b2402144Bb366A632D14B83F244D2e0e21bD39c |
| Avalanche | 0x0e082F06FF657D94310cB8cE8B0D9a04541d8052 |
| Base | 0x8d2de8d2f73F1F4cAB472AC9A881C9b123C79627 |
| Berachain | 0x3Ff72741fd67D6AD0668d93B41a09248F4700560 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0xB6F6D86a8f9879A9c87f643768d9efc38c1Da6E7 |
| Celo | 0x796Dff6D74F3E27060B71255Fe517BFb23C93eed |
| Fantom | 0x7C9Fc5741288cDFdD83CeB07f3ea7e22618D79D2 |
| Injective | inj1ghd753shjuwexxywmgs4xz7x2q732vcnxxynfn |
| Ink | 0x3Ff72741fd67D6AD0668d93B41a09248F4700560 |
| Kaia | 0x5b08ac39EAED75c0439FC750d9FE7E1F9dD0193F |
| Linea | 0x167E0752de62cb76EFc0Fbb165Bd342c6e2Bb251 |
| Mantle | 0x24850c6f61C438823F01B7A3BF2B89B72174Fa9d |
| Moonbeam | 0xb1731c586ca89a23809861c6103f0b96b3f57d92 |
| NEAR | contract.portalbridge.near |
| Optimism | 0x1D68124e65faFC907325e3EDbF8c4d84499DAa8b |
| Polygon | 0x5a58505a96D1dbf8dF91cB21B54419FC36e93fdE |
| Scroll | 0x24850c6f61C438823F01B7A3BF2B89B72174Fa9d |
| Sei | sei1smzlm9t79kur392nu9egl8p8je9j92q4gzguewj56a05kyxxra0qy0nuf3 |
| Seievm | 0x3Ff72741fd67D6AD0668d93B41a09248F4700560 |
| Sui | 0xc57508ee0d4595e5a8728974a4a93a787d38f339757230d441e895422c07aba9 |
| Unichain | 0x3Ff72741fd67D6AD0668d93B41a09248F4700560 |
| World Chain | 0xc309275443519adca74c9136b02A38eF96E3a1f6 |
| X Layer | 0x5537857664B0f9eFe38C9f320F75fEf23234D904 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x47F5195163270345fb4d7B9319Eda8C64C75E278 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Holesky | 0x76d093BbaE4529a342080546cAFEec4AcbA59EC6 |
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0xDB5492265f6038831E89f495670FF909aDe94bd9 |
| Solana | DZnkkTmCiFWfYTfT41X3Rd1kDgozqzxWaHqsw6W4x2oe |
| Algorand | 86525641 |
| Aptos | 0x576410486a2da45eee6c949c995670112ddf2fbeedab20350d506328eefc9d4f |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xC7A204bDBFe983FCD8d8E61D02b475D4073fF97e |
| Avalanche | 0x61E44E506Ca5659E6c0bba9b678586fA2d729756 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x86F55A04690fd7815A3D802bD587e83eA888B239 |
| Berachain | 0xa10f2eF61dE1f19f586ab8B6F2EbA89bACE63F7a |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x9dcF9D205C9De35334D646BeE44b2D2859712A09 |
| Celo | 0x05ca6037eC51F8b712eD2E6Fa72219FEaE74E153 |
| Fantom | 0x599CEa2204B4FaECd584Ab1F2b6aCA137a0afbE8 |
| Fogo | 78HdStBqCMioGii9D8mF3zQaWDqDZBQWTUwjjpdmbJKX |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0x4a8bc80Ed5a4067f1CCf107057b8270E0cC11A78 |
| Injective | inj1q0e70vhrv063eah90mu97sazhywmeegp7myvnh |
| Ink | 0x376428e7f26D5867e69201b275553C45B09EE090 |
| Kaia | 0xC7A13BE098720840dEa132D860fDfa030884b09A |
| Linea | 0xC7A204bDBFe983FCD8d8E61D02b475D4073fF97e |
| Mantle | 0x75Bfa155a9D7A3714b0861c8a8aF0C4633c45b5D |
| Mezo | 0xA31aa3FDb7aF7Db93d18DDA4e19F811342EDF780 |
| Monad | 0xF323dcDe4d33efe83cf455F78F9F6cc656e6B659 |
| Moonbeam | 0xbc976D4b9D57E57c3cA52e1Fd136C45FF7955A96 |
| NEAR | token.wormhole.testnet |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x99737Ec4B815d816c49A385943baf0380e75c0Ac |
| Polygon Amoy | 0xC7A204bDBFe983FCD8d8E61D02b475D4073fF97e |
| Scroll | 0x22427d90B7dA3fA4642F7025A854c7254E4e45BF |
| Sei | sei1jv5xw094mclanxt5emammy875qelf3v62u4tl4lp5nhte3w3s9ts9w9az2 |
| Seievm | 0x23908A62110e21C04F3A4e011d24F901F911744A |
| Sui | 0x6fb10cdb7aa299e9a4308752dadecb049ff55a892de92992a1edbd7912b3d6da |
| Unichain | 0xa10f2eF61dE1f19f586ab8B6F2EbA89bACE63F7a |
| World Chain | 0x430855B4D43b8AEB9D2B9869B74d58dda79C0dB2 |
| X Layer | 0xdA91a06299BBF302091B053c6B9EF86Eff0f930D |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x7d8eBc211C4221eA18E511E4f0fD50c5A539f275 |
=== "Devnet"
| Ethereum | 0x0290FB167208Af455bB137780163b7B7a9a10C16 |
| Solana | B6RHG3mfcckmrYN1UhmJzyS1XX3fZKbkeUcpJe9Sy3FE |
| Algorand | 1006 |
| Aptos | 0x84a5f374d29fc77e370014dce4fd6a55b58ad608de8074b0be5571701724da31 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x0290FB167208Af455bB137780163b7B7a9a10C16 |
| NEAR | token.test.near |
| Sui | 0xa6a3da85bbe05da5bfd953708d56f1a3a023e7fb58e5a824a3d4de3791e8f690 |
## Wormhole Relayer
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Arbitrum | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Avalanche | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Base | 0x706f82e9bb5b0813501714ab5974216704980e31 |
| Berachain | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Celo | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Fantom | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Ink | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Kaia | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Mantle | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Mezo | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Moonbeam | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Optimism | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Plume | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Polygon | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Scroll | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Seievm | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| Unichain | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
| World Chain | 0x1520cc9e779c56dab5866bebfb885c86840c33d3 |
| X Layer | 0x27428DD2d3DD32A4D7f7C497eAaa23130d894911 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x7B1bD7a6b4E61c2a123AC6BC2cbfC614437D0470 |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0x7B1bD7a6b4E61c2a123AC6BC2cbfC614437D0470 |
| Avalanche | 0xA3cF45939bD6260bcFe3D66bc73d60f19e49a8BB |
| Base Sepolia | 0x93BAD53DDfB6132b0aC8E37f6029163E63372cEE |
| Berachain | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x80aC94316391752A193C1c47E27D382b507c93F3 |
| Celo | 0x306B68267Deb7c5DfCDa3619E22E9Ca39C374f84 |
| Fantom | 0x7B1bD7a6b4E61c2a123AC6BC2cbfC614437D0470 |
| Ink | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
| Mezo | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
| Monad | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
| Moonbeam | 0x0591C25ebd0580E0d4F27A82Fc2e24E7489CB5e0 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x93BAD53DDfB6132b0aC8E37f6029163E63372cEE |
| Polygon Amoy | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
| Seievm | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
| Unichain | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x362fca37E45fe1096b42021b543f462D49a5C8df |
=== "Devnet"
| Ethereum | 0xcC680D088586c09c3E0E099a676FA4b6e42467b4 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0xcC680D088586c09c3E0E099a676FA4b6e42467b4 |
## CCTP
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0xAaDA05BD399372f0b0463744C09113c137636f6a |
| Arbitrum | 0x2703483B1a5a7c577e8680de9Df8Be03c6f30e3c |
| Avalanche | 0x09Fb06A271faFf70A651047395AaEb6265265F13 |
| Base | 0x03faBB06Fa052557143dC28eFCFc63FC12843f1D |
| Optimism | 0x2703483B1a5a7c577e8680de9Df8Be03c6f30e3c |
| Polygon | 0x0FF28217dCc90372345954563486528aa865cDd6 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x2703483B1a5a7c577e8680de9Df8Be03c6f30e3c |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0x2703483B1a5a7c577e8680de9Df8Be03c6f30e3c |
| Avalanche | 0x58f4c17449c90665891c42e14d34aae7a26a472e |
| Base Sepolia | 0x2703483B1a5a7c577e8680de9Df8Be03c6f30e3c |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x2703483B1a5a7c577e8680de9Df8Be03c6f30e3c |
## Settlement Token Router
=== "Mainnet"
| Chain Name | Contract Address |
|---|
| Ethereum | 0x70287c79ee41C5D1df8259Cd68Ba0890cd389c47 |
| Solana | 28topqjtJzMnPaGFmmZk68tzGmj9W9aMntaEK3QkgtRe |
| Arbitrum | 0x70287c79ee41C5D1df8259Cd68Ba0890cd389c47 |
| Avalanche | 0x70287c79ee41C5D1df8259Cd68Ba0890cd389c47 |
| Base | 0x70287c79ee41C5D1df8259Cd68Ba0890cd389c47 |
| Optimism | 0x70287c79ee41C5D1df8259Cd68Ba0890cd389c47 |
| Polygon | 0x70287c79ee41C5D1df8259Cd68Ba0890cd389c47 |
=== "Testnet"
| Chain Name | Contract Address |
|---|
| Solana | tD8RmtdcV7bzBeuFgyrFc8wvayj988ChccEzRQzo6md |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xe0418C44F06B0b0D7D1706E01706316DBB0B210E |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x6BAa7397c18abe6221b4f6C3Ac91C88a9faE00D8 |
## Executor
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x84EEe8dBa37C36947397E1E11251cA9A06Fc6F8a |
| Solana | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Aptos | 0x11aa75c059e1a7855be66b931bf340a2e0973274ac16b5f519c02ceafaf08a18 |
| Arbitrum | 0x3980f8318fc03d79033Bbb421A622CDF8d2Eeab4 |
| Avalanche | 0x4661F0E629E4ba8D04Ee90080Aee079740B00381 |
| Base | 0x9E1936E91A4a5AE5A5F75fFc472D6cb8e93597ea |
| Berachain | 0x0Dd7a5a32311b8D87A615Cc7f079B632D3d5e2D3 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0xeC8cCCD058DbF28e5D002869Aa9aFa3992bf4ee0 |
| Celo | 0xe6Ea5087c6860B94Cf098a403506262D8F28cF05 |
| CreditCoin | 0xd2e420188f17607Aa6344ee19c3e76Cf86CA7BDe |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0xd7717899cc4381033Bc200431286D0AC14265F78 |
| Ink | 0x3e44a5F45cbD400acBEF534F51e616043B211Ddd |
| Linea | 0x23aF2B5296122544A9A7861da43405D5B15a9bD3 |
| Mezo | 0x0f9b8E144Cc5C5e7C0073829Afd30F26A50c5606 |
| Moonbeam | 0x85D06449C78064c2E02d787e9DC71716786F8D19 |
| Optimism | 0x85B704501f6AE718205C0636260768C4e72ac3e7 |
| Polygon | 0x0B23efA164aB3eD08e9a39AC7aD930Ff4F5A5e81 |
| Scroll | 0xcFAdDE24640e395F5A71456A825D0D7C3741F075 |
| Seievm | 0x25f1c923fb7a5aefa5f0a2b419fc70f2368e66e5 |
| Sonic | 0x3Fdc36b4260Da38fBDba1125cCBD33DD0AC74812 |
| Sui | 0xdb0fe8bb1e2b5be628adbea0636063325073e1070ee11e4281457dfd7f158235 |
| Unichain | 0x764dD868eAdD27ce57BCB801E4ca4a193d231Aed |
| World Chain | 0x8689b4E6226AdC8fa8FF80aCc3a60AcE31e8804B |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x8345E90Dcd92f5Cf2FAb0C8E2A56A5bc2c30d896 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0xD0fb39f5a3361F21457653cB70F9D0C9bD86B66B |
| Solana | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Aptos | 0x139717c339f08af674be77143507a905aa28cbc67a0e53e7095c07b630d73815 |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xBF161de6B819c8af8f2230Bcd99a9B3592f6F87b |
| Avalanche | 0x4661F0E629E4ba8D04Ee90080Aee079740B00381 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x51B47D493CBA7aB97e3F8F163D6Ce07592CE4482 |
| Converge | 0xAab9935349B9c08e0e970720F6D640d5B91C293E |
| Fogo | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Mezo | 0x0f9b8E144Cc5C5e7C0073829Afd30F26A50c5606 |
| Monad | 0xC04dE634982cAdF2A677310b73630B7Ac56A3f65 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x5856651eB82aeb6979B4954317194d48e1891b3c |
| Plume | 0x8fc2FbA8F962fbE89a9B02f03557a011c335A455 |
| Seievm | 0x25f1c923Fb7A5aEFA5F0A2b419fC70f2368e66e5 |
| Sui | 0x4000cfe2955d8355b3d3cf186f854fea9f787a457257056926fde1ec977670eb |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x4d9525D94D275dEB495b7C8840b154Ae04cfaC2A |
## Guardian Governance
=== "Mainnet"
| Solana | NGoD1yTeq5KaURrZo7MnCTFzTA4g62ygakJCnzMLCfm |
| Ethereum | 0x23Fea5514DFC9821479fBE18BA1D7e1A61f6FfCf |
| Arbitrum | 0x36CF4c88FA548c6Ad9fcDc696e1c27Bb3306163F |
| Avalanche | 0x169D91C797edF56100F1B765268145660503a423 |
| Base | 0x838a95B6a3E06B6f11C437e22f3C7561a6ec40F1 |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0x574B7864119C9223A9870Ea614dC91A8EE09E512 |
| Optimism | 0x0E09a3081837ff23D2e59B179E0Bc48A349Afbd8 |
| Unichain | 0x574b7864119c9223a9870ea614dc91a8ee09e512 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x574B7864119C9223A9870Ea614dC91A8EE09E512 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x9517F0164c1d089ad72E669E57b9088790966dBd |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0x81b65A48DCAccBA04aCa3C055C4112b0715b90c0 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x720A59128B96Eda6EC2940c7899406E4dc56d0DC |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0xcE1DE1eA4b040D324a07719043A6234C94fd0b5d |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x574B7864119C9223A9870Ea614dC91A8EE09E512 |
!!! note
Guardian-governed ownership contracts are used where an owner is required, without adding new trust assumptions. They only accept instructions signed by a quorum of Wormhole Guardians, validated on-chain by the Wormhole Core contracts. Implementations: [EVM](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/native-token-transfers/blob/main/evm/src/wormhole/Governance.sol){target=\_blank} and [SVM](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/native-token-transfers/blob/main/solana/programs/wormhole-governance/src/instructions/governance.rs){target=\_blank}.
## Read-Only Deployments
=== "Mainnet"
| Acala | 0xa321448d90d4e5b0A732867c18eA198e75CAC48E |
| Aurora | 0x51b5123a7b0F9b2bA265f9c4C8de7D78D52f510F |
| Blast | 0xbebdb6C8ddC678FfA9f8748f85C815C556Dd8ac6 |
| Corn | 0xa683c66045ad16abb1bCE5ad46A64d95f9A25785 |
| Gnosis | 0xa321448d90d4e5b0A732867c18eA198e75CAC48E |
| Goat | 0x352A86168e6988A1aDF9A15Cb00017AAd3B67155 |
| Karura | 0xa321448d90d4e5b0A732867c18eA198e75CAC48E |
| LightLink | 0x352A86168e6988A1aDF9A15Cb00017AAd3B67155 |
| Oasis | 0xfE8cD454b4A1CA468B57D79c0cc77Ef5B6f64585 |
| Rootstock | 0xbebdb6C8ddC678FfA9f8748f85C815C556Dd8ac6 |
| Sonic | 0x352A86168e6988A1aDF9A15Cb00017AAd3B67155 |
| Telos | 0x352A86168e6988A1aDF9A15Cb00017AAd3B67155 |
| Terra | terra1dq03ugtd40zu9hcgdzrsq6z2z4hwhc9tqk2uy5 |
| Terra 2.0 | terra12mrnzvhx3rpej6843uge2yyfppfyd3u9c3uq223q8sl48huz9juqffcnhp |
| SNAXchain | 0xc1BA3CC4bFE724A08FbbFbF64F8db196738665f4 |
| XPLA | xpla1jn8qmdda5m6f6fqu9qv46rt7ajhklg40ukpqchkejcvy8x7w26cqxamv3w |
!!! note
Read-only deployments allow Wormhole messages to be received on chains not fully integrated with Wormhole Guardians. These deployments support cross-chain data verification but cannot originate messages. For example, a governance message can be sent from a fully integrated chain and processed on a read-only chain, but the read-only chain cannot send messages back.
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/executor-addresses.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Executor Addresses
description: Reference list of deployed Executor contract addresses across integrations, including CCTP, NTT, WTT, and referrer variants.
categories: Reference
---
# Executor Addresses
## Executor
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x84EEe8dBa37C36947397E1E11251cA9A06Fc6F8a |
| Solana | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Aptos | 0x11aa75c059e1a7855be66b931bf340a2e0973274ac16b5f519c02ceafaf08a18 |
| Arbitrum | 0x3980f8318fc03d79033Bbb421A622CDF8d2Eeab4 |
| Avalanche | 0x4661F0E629E4ba8D04Ee90080Aee079740B00381 |
| Base | 0x9E1936E91A4a5AE5A5F75fFc472D6cb8e93597ea |
| Berachain | 0x0Dd7a5a32311b8D87A615Cc7f079B632D3d5e2D3 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0xeC8cCCD058DbF28e5D002869Aa9aFa3992bf4ee0 |
| Celo | 0xe6Ea5087c6860B94Cf098a403506262D8F28cF05 |
| CreditCoin | 0xd2e420188f17607Aa6344ee19c3e76Cf86CA7BDe |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0xd7717899cc4381033Bc200431286D0AC14265F78 |
| Ink | 0x3e44a5F45cbD400acBEF534F51e616043B211Ddd |
| Linea | 0x23aF2B5296122544A9A7861da43405D5B15a9bD3 |
| Mezo | 0x0f9b8E144Cc5C5e7C0073829Afd30F26A50c5606 |
| Moonbeam | 0x85D06449C78064c2E02d787e9DC71716786F8D19 |
| Optimism | 0x85B704501f6AE718205C0636260768C4e72ac3e7 |
| Polygon | 0x0B23efA164aB3eD08e9a39AC7aD930Ff4F5A5e81 |
| Scroll | 0xcFAdDE24640e395F5A71456A825D0D7C3741F075 |
| Seievm | 0x25f1c923fb7a5aefa5f0a2b419fc70f2368e66e5 |
| Sonic | 0x3Fdc36b4260Da38fBDba1125cCBD33DD0AC74812 |
| Sui | 0xdb0fe8bb1e2b5be628adbea0636063325073e1070ee11e4281457dfd7f158235 |
| Unichain | 0x764dD868eAdD27ce57BCB801E4ca4a193d231Aed |
| World Chain | 0x8689b4E6226AdC8fa8FF80aCc3a60AcE31e8804B |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x8345E90Dcd92f5Cf2FAb0C8E2A56A5bc2c30d896 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0xD0fb39f5a3361F21457653cB70F9D0C9bD86B66B |
| Solana | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Aptos | 0x139717c339f08af674be77143507a905aa28cbc67a0e53e7095c07b630d73815 |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xBF161de6B819c8af8f2230Bcd99a9B3592f6F87b |
| Avalanche | 0x4661F0E629E4ba8D04Ee90080Aee079740B00381 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x51B47D493CBA7aB97e3F8F163D6Ce07592CE4482 |
| Converge | 0xAab9935349B9c08e0e970720F6D640d5B91C293E |
| Fogo | execXUrAsMnqMmTHj5m7N1YQgsDz3cwGLYCYyuDRciV |
| Mezo | 0x0f9b8E144Cc5C5e7C0073829Afd30F26A50c5606 |
| Monad | 0xC04dE634982cAdF2A677310b73630B7Ac56A3f65 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x5856651eB82aeb6979B4954317194d48e1891b3c |
| Plume | 0x8fc2FbA8F962fbE89a9B02f03557a011c335A455 |
| Seievm | 0x25f1c923Fb7A5aEFA5F0A2b419fC70f2368e66e5 |
| Sui | 0x4000cfe2955d8355b3d3cf186f854fea9f787a457257056926fde1ec977670eb |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x4d9525D94D275dEB495b7C8840b154Ae04cfaC2A |
## CCTP With Executor
=== "Mainnet v1"
| Ethereum | 0xeEFb36c4458dA7798742cf038C5c27E07aB9c51E |
| Solana | CXGRA5SCc8jxDbaQPZrmmZNu2JV34DP7gFW4m31uC1zs |
| Arbitrum | 0x55Dd4466BFec29527C54A72fd306efb54e5F7027 |
| Avalanche | 0xd331819478b74d8a7B8EA631118B4a4e50F6EbD1 |
| Aptos | 0x9f5ad7d5c2d067ca4abb6d8d6aba44c15596b71a1def8eb4596089b527bb2eb1 |
| Base | 0x08FEB1838C3d7F8509DA1EBb9a11a94c1f006cb2 |
| Optimism | 0xBC6f9d1CBa49DB365728478cefa02F6743617637 |
| Polygon | 0x007995f2AEcfBC745f20a7AE8D3a02c0EbF46264 |
| Unichain | 0xA7aBDb8f2108901c586543BD5e10E4fA263F4A47 |
=== "Testnet v1"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x0F78904c750801391EbBf308181e9d6fc892B0f3 |
| Solana Devnet | CXGRA5SCc8jxDbaQPZrmmZNu2JV34DP7gFW4m31uC1zs |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xc9c0A1030331D5dA0599D243eFd4682D906066D9 |
| Avalanche Fuji | 0x2cfEC91B50f657Cc86Ec693542527ac3e03bF742 |
| Aptos | 0x14a12d1fd6ef371b70c2113155534ec152ec7f779e281b54866c796c9a4a58d3? |
| Base Sepolia | 0x4983C6bD3bB7DA9EECe71cfa7AE4C67CAbf362F0 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0x1F2e73E9AF5eecEdAF03b4F295f83BD587290867 |
=== "Mainnet v2"
| Ethereum | 0x2cCf230467FE7387674BAa657747F0B5485c7fEC |
| Solana | Supported |
| Arbitrum | 0x8442d68524217601ed126f6859694e4b0c7c66a1 |
| Avalanche | 0x3952914628650Ca510404872D84DfF10A844C5B5 |
| Base | 0xbd8d42f40a11b37bD1b3770D754f9629F7cd5679 |
| Codex | 0xE1Df8709CAa70c5eCEa0c27871cA7029Fcb0A0bd |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0xACD054f83c0b852d02503191e2c26527A7E72B1f |
| Ink | 0xD64341A38a5eAfb9EB9BACf8A5C52Fe858c4ABE9 |
| Linea | 0xc48c126468BE919068dE1983F00F65af759a4E87 |
| Optimism | 0xd0a8940b2e743e33b682daec4d52b46713606c9d |
| Plume | 0x486228859880ec6c05175035bEe2e5383D23B0fE |
| Polygon | 0xc8a8e6d760dcbd5d6746e2f66cd2ffa722dd1e59 |
| Seievm | 0xf4FefFc03EEFB06B009bFB168b60B30edf7abc12 |
| Sonic | 0xc39BF082ec91D9bC385F956D24a8D66C0c26223d |
| Unichain | 0xD5D5D640D8b758672Cc7A078734175c4433866d5 |
| World Chain | 0x789f2b91f7B35D5B890983328340c4600339B354 |
=== "Testnet v2"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x0F18DD26D0B41fb1eaa9cF34D1Ec6022aA69a8e2 |
| Solana Devnet | CXGRA5SCc8jxDbaQPZrmmZNu2JV34DP7gFW4m31uC1zs |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xC92946F22eA76bcB5Ee020525aC32d2098040570 |
| Avalanche Fuji | 0x4058F0C3924eDaB19c15597C438968ed49C1a213 |
| Base Sepolia | 0xC400FcC0e92d3406747FBb6f513D3aa8B038fcE9 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0xCCA1Cb361E3206faFcDBaCD99e02b32d730cf695 |
## NTT With Executor
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0xD2D9c936165a85F27a5a7e07aFb974D022B89463 |
| Solana | nex1gkSWtRBheEJuQZMqHhbMG5A45qPU76KqnCZNVHR |
| Arbitrum | 0x0Af42A597b0C201D4dcf450DcD0c06d55ddC1C77 |
| Avalanche | 0x4e9Af03fbf1aa2b79A2D4babD3e22e09f18Bb8EE |
| Base | 0x83216747fC21b86173D800E2960c0D5395de0F30 |
| Berachain | 0x0a2AF374Cc9CCCbB0Acc4E34B20b9d02a0f08c30 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x39B57Dd9908F8be02CfeE283b67eA1303Bc29fe1 |
| Celo | 0x3d69869fcB9e1CD1F4020b637fb8256030BAc8fC |
| CreditCoin | 0x5454b995719626256C96fb57454b044ffb3Da2F9 |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | 0x431017B1718b86898C7590fFcCC380DEf0456393 |
| Ink | 0x420370DC2ECC4D44b47514B7859fd11809BbeFF5 |
| Linea | 0xEAa5AddB5b8939Eb73F7faF46e193EefECaF13E9 |
| Mezo | 0x484b5593BbB90383f94FB299470F09427cf6cfE2 |
| Moonbeam | 0x1365593C8bae71a55e48E105a2Bb76d5928c7DE3 |
| Monad | 0x93FE94Ad887a1B04DBFf1f736bfcD1698D4cfF66Multi Ntt:0xFEA937F7124E19124671f1685671d3f04a9Af4E4 |
| Optimism | 0x85C0129bE5226C9F0Cf4e419D2fefc1c3FCa25cF |
| Plume | 0x6Eb53371f646788De6B4D0225a4Ed1d9267188AD |
| Polygon | 0x6762157b73941e36cEd0AEf54614DdE545d0F990 |
| Scroll | 0x055625d48968f99409244E8c3e03FbE73B235a62 |
| Seievm | 0x3F2D6441C7a59Dfe80f8e14142F9E28F6D440445 |
| Sonic | 0xaCa00703bb87F31D6F9fCcc963548b48FA46DfeB |
| Unichain | 0x607723D6353Dae3ef62B7B277Cfabd0F4bc6CB4C |
| World Chain | 0x66b1644400D51e104272337226De3EF1A820eC79 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x6bBd1ff3bB303F88835A714EE3241bF45DE26d29 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x54DD7080aE169DD923fE56d0C4f814a0a17B8f41 |
| Solana Devnet | nex1gkSWtRBheEJuQZMqHhbMG5A45qPU76KqnCZNVHR |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xd048170F1ECB8D47E499D3459aC379DA023E2C1B |
| Avalanche Fuji | 0x4e9Af03fbf1aa2b79A2D4babD3e22e09f18Bb8EE |
| Base Sepolia | 0x5845E08d890E21687F7Ebf7CbAbD360cD91c6245 |
| Celo | 0x3d69869fcB9e1CD1F4020b637fb8256030BAc8fC |
| Converge | 0x3d8c26b67BDf630FBB44F09266aFA735F1129197 |
| Fogo | nex1gkSWtRBheEJuQZMqHhbMG5A45qPU76KqnCZNVHR |
| Mezo | 0x484b5593BbB90383f94FB299470F09427cf6cfE2 |
| Monad | 0x93FE94Ad887a1B04DBFf1f736bfcD1698D4cfF66 |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0xaDB1C56D363FF5A75260c3bd27dd7C1fC8421EF5 |
| Plume | 0x6Eb53371f646788De6B4D0225a4Ed1d9267188AD |
| Seievm | 0x3F2D6441C7a59Dfe80f8e14142F9E28F6D440445 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0xcDD9d7C759b29680f7a516d0058de8293b2AC7b1 |
## WTT Executor
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0xa8969F3f8D97b3Ed89D4e2EC19B6B0CfD504b212 |
| Solana | tbr7Qje6qBzPwfM52csL5KFi8ps5c5vDyiVVBLYVdRf |
| Arbitrum | 0x04C98824a64d75CD1E9Bc418088b4c9A99048153 |
| Avalanche | 0x8849F05675E034b54506caB84450c8C82694a786 |
| Base | 0xD8B736EF27Fc997b1d00F22FE37A58145D3BDA07 |
| Berachain | 0xFAeFa20CB3759AEd2310E25015F05d62D8567A3F |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x2513515340fF71DD5AF02fC1BdB9615704d91524 |
| Celo | 0xe478DEe705BEae591395B08934FA19F54df316BE |
| Fantom | 0xcafd2f0a35a4459fa40c0517e17e6fa2939441ca |
| Ink | 0x4bFB47F4c8A904d2C24e73601D175FE3a38aAb5B |
| Moonbeam | 0xF6b9616C63Fa48D07D82c93CE02B5d9111c51a3d |
| Optimism | 0x37aC29617AE74c750a1e4d55990296BAF9b8De73 |
| Polygon | 0x1d98CA4221516B9ac4869F5CeA7E6bb9C41609D6 |
| Scroll | 0x05129e142e7d5A518D81f19Db342fBF5f7E26A18 |
| Seievm | 0x7C129bc8F6188d12c0d1BBDE247F134148B97618 |
| Sui | 0x57f4e0ba41a7045e29d435bc66cc4175f381eb700e6ec16d4fdfe92e5a4dff9f |
| Unichain | 0x9Bca817F67f01557aeD615130825A28F4C5f3b87 |
| World Chain | 0xc0565Bd29b34603C0383598E16843d95Ae9c4f65 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x37bCc9d175124F77Bfce68589d2a8090eF846B85 |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0xb0b2119067cF04fa959f654250BD49fE1BD6F53c |
| Solana | tbr7Qje6qBzPwfM52csL5KFi8ps5c5vDyiVVBLYVdRf |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | 0xaE8dc4a7438801Ec4edC0B035EcCCcF3807F4CC1 |
| Avalanche | 0x10Ce9a35883C44640e8B12fea4Cc1e77F77D8c52 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x523d25D33B975ad72283f73B1103354352dBCBb8 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Celo | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Fantom | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Fogo | tbr7Qje6qBzPwfM52csL5KFi8ps5c5vDyiVVBLYVdRf |
| Mezo | 0x2002a44b1106DF83671Fb419A2079a75e2a34808 |
| Monad | 0x5Ba2c39cF0624BB5fBe94E919519aEA0DdD68454 |
| Moonbeam | 0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b |
| Optimism Sepolia | 0xaE8dc4a7438801Ec4edC0B035EcCCcF3807F4CC1 |
| Sui | 0xb30040e5120f8cb853b691cb6d45981ae884b1d68521a9dc7c3ae881c0031923 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0xb00224c60fe6ab134c8544dc29350286545f8dcc |
## WTT Executor With Referrer
=== "Mainnet"
| Ethereum | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Arbitrum | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Avalanche | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Base | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Berachain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| BNB Smart Chain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Celo | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Ink | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Moonbeam | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Optimism | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Polygon | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Scroll | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Seievm | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Unichain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| World Chain | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x13a35c075D6Acc1Fb9BddFE5FE38e7672789e4db |
=== "Testnet"
| Ethereum Sepolia | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Avalanche | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Base Sepolia | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Mezo | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| Monad | 0x412f30e9f8B4a1e99eaE90209A6b00f5C3cc8739 |
| XRPL-EVM | 0x17CFAAf9e8a5ABb1eee758dB9040F945c9EAC907 |
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/supported-networks.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Supported Networks
description: Learn about the networks each Wormhole product supports, and explore links to documentation, official websites, and block explorers.
categories: Reference
---
# Supported Networks
Wormhole supports many blockchains across mainnet, testnet, and devnets. You can use these tables to verify if your desired chains are supported by the Wormhole products you plan to include in your integration.
## Supported Networks by Product
### Connect
| Ethereum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Solana | SVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Aptos | Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Arbitrum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Avalanche | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Base | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Berachain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| BNB Smart Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Celo | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Fantom | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mantle | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mezo | EVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Moonbeam | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Optimism | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Osmosis | CosmWasm | :x: | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Polygon | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Scroll | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sui | Sui Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Unichain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| World Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| X Layer | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
### NTT
| Ethereum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Solana | SVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Arbitrum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Avalanche | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Base | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Berachain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| BNB Smart Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Celo | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Converge | EVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website |
| CreditCoin | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Fantom | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Fogo | SVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs |
| Ink | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Kaia | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Linea | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mantle | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mezo | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Monad | EVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Moonbeam | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Optimism | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Plume | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Polygon | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Scroll | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Seievm | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sui | Sui Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Unichain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| World Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| X Layer | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| XRPL-EVM | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
### WTT
| Ethereum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Solana | SVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Algorand | AVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Aptos | Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Arbitrum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Avalanche | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Base | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Berachain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| BNB Smart Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Celo | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Fantom | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Fogo | SVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | EVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs |
| Injective | CosmWasm | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Ink | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Kaia | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Linea | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mantle | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mezo | EVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Monad | EVM | :x: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Moonbeam | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| NEAR | NEAR VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Optimism | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Polygon | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Scroll | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sei | CosmWasm | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Seievm | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sui | Sui Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Unichain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| World Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| X Layer | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| XRPL-EVM | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
### CCTP
| Ethereum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Solana | SVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Aptos | Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Arbitrum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Avalanche | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Base | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| HyperCore | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs |
| Ink | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Linea | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Optimism | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Plume | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Polygon | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Seievm | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sonic | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sui | Sui Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Unichain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| World Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
### Settlement
| Ethereum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Solana | SVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Arbitrum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Avalanche | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Base | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Optimism | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Polygon | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sui | Sui Move VM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Unichain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :x: | :x: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
### Multigov
| Ethereum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Solana | SVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Arbitrum | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Avalanche | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Base | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Berachain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| BNB Smart Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Celo | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Converge | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website |
| CreditCoin | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Fantom | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| HyperCore | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs |
| Ink | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Kaia | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Linea | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mantle | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Mezo | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Monad | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Moonbeam | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Optimism | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Plasma | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Plume | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Polygon | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Scroll | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sei | CosmWasm | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Seievm | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Sonic | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| Unichain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| World Chain | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| X Layer | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
| XRPL-EVM | EVM | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: | :material-web:Website:material-file-document:Developer Docs:octicons-package-16:Block Explorer |
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/testnet-faucets.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Testnet Faucets
description: This page includes resources to quickly find the Testnet tokens you need to deploy and test applications and contracts on Wormhole's supported networks.
categories: Reference
---
# Testnet Faucets
Don't let the need for testnet tokens get in the way of buildling your next great idea with Wormhole. Use this guide to quickly locate the testnet token faucets you need to deploy and test applications and contracts on Wormhole's supported networks.
### EVM
| Ethereum Holesky | EVM | ETH | Alchemy Faucet |
| Ethereum Sepolia | EVM | ETH | Alchemy Faucet |
| Arbitrum Sepolia | EVM | ETH | List of Faucets |
| Avalanche | EVM | AVAX | Official Avalanche Faucet |
| Base Sepolia | EVM | ETH | List of Faucets |
| Berachain | EVM | BERA | Official Berachain Faucet |
| BNB Smart Chain | EVM | BNB | Official BNB Faucet |
| Celo | EVM | CELO | Official Celo Faucet |
| Fantom | EVM | FTM | Official Fantom Faucet |
| HyperEVM :material-alert:{ title='⚠️ The HyperEVM integration is experimental, as its node software is not open source. Use Wormhole messaging on HyperEVM with caution.' } | EVM | mock USDC | Official Hyperliquid Faucet |
| Ink | EVM | ETH | Official Ink Faucet |
| Kaia | EVM | KAIA | Official Kaia Faucet |
| Linea | EVM | ETH | List of Faucets |
| Mantle | EVM | MNT | Official Mantle Faucet |
| Monad | EVM | MON | Official Monad Faucet |
| Moonbeam | EVM | DEV | Official Moonbeam Faucet |
| Optimism Sepolia | EVM | ETH | Superchain Faucet |
| Plasma | EVM | XPL | Plasma Faucet |
| Plume | EVM | PLUME | Official Plume Faucet |
| Polygon Amoy | EVM | POL | Official Polygon Faucet |
| Scroll | EVM | ETH | List of Faucets |
| Seievm | EVM | SEI | Sei Atlantic-2 Faucet |
| Unichain | EVM | ETH | QuickNode Faucet |
| World Chain | EVM | ETH | Alchemy Faucet |
| X Layer | EVM | OKB | X Layer Official Faucet |
| XRPL-EVM | EVM | XRP | XRPL Official Faucet |
### SVM
| Pythnet | SVM | ETH | Superchain Faucet |
### AVM
| Algorand | AVM | ALGO | Official Algorand Faucet |
### CosmWasm
| Celestia | CosmWasm | TIA | Discord Faucet |
| Cosmos Hub | CosmWasm | ATOM | Discord Faucet |
| Injective | CosmWasm | INJ | Official Injective Faucet |
| Kujira | CosmWasm | KUJI | Discord Faucet |
| Neutron | CosmWasm | NTRN | List of Faucets |
| Noble | CosmWasm | USDC | Circle Faucet |
| Osmosis | CosmWasm | OSMO | Official Osmosis Faucet |
| SEDA | CosmWasm | SEDA | Official SEDA Faucet |
| Sei | CosmWasm | SEI | Sei Atlantic-2 Faucet |
### Move VM
| Aptos | Move VM | APT | Official Aptos Faucet |
### NEAR VM
| NEAR | NEAR VM | NEAR | Official NEAR Faucet |
### Sui Move VM
| Sui | Sui Move VM | SUI | List of Faucets |
--- END CONTENT ---
Doc-Content: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-docs/refs/heads/main/products/reference/wormhole-formatted-addresses.md
--- BEGIN CONTENT ---
---
title: Wormhole Formatted Addresses
description: Explanation of Wormhole formatted 32-byte hex addresses, their conversion, and usage across different blockchain platforms.
categories: Reference
---
# Wormhole Formatted Addresses
Wormhole formatted addresses are 32-byte hex representations of addresses from any supported blockchain. Whether an address originates from EVM, Solana, Cosmos, or another ecosystem, Wormhole standardizes all addresses into this format to ensure cross-chain compatibility.
This uniform format is essential for smooth interoperability in token transfers and messaging across chains. Wormhole uses formatted addresses throughout the [Wormhole SDK](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-sdk-ts){target=\_blank}, especially in cross-chain transactions, such as transfer functions that utilize the `bytes32` representation for recipient addresses.
## Platform-Specific Address Formats
Each blockchain ecosystem Wormhole supports has its method for formatting native addresses. To enable cross-chain compatibility, Wormhole converts these native addresses into the standardized 32-byte hex format.
Here’s an overview of the native address formats and how they are normalized to the Wormhole format:
| Platform | Native Address Format | Wormhole Formatted Address |
|-----------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------|
| EVM | Hex (e.g., 0x...) | 32-byte Hex |
| Solana | Base58 | 32-byte Hex |
| CosmWasm | Bech32 | 32-byte Hex |
| Algorand | Algorand App ID | 32-byte Hex |
| Sui | Hex | 32-byte Hex |
| Aptos | Hex | 32-byte Hex |
| Near | SHA-256 | 32-byte Hex |
These conversions allow Wormhole to interact seamlessly with various chains using a uniform format for all addresses.
### Address Format Handling
The Wormhole SDK provides mappings that associate each platform with its native address format. You can find this mapping in the Wormhole SDK file [`platforms.ts`](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-sdk-ts/blob/007f61b27c650c1cf0fada2436f79940dfa4f211/core/base/src/constants/platforms.ts#L93-L102){target=\_blank}:
```typescript
const platformAddressFormatEntries = [
['Evm', 'hex'],
['Solana', 'base58'],
['Cosmwasm', 'bech32'],
['Algorand', 'algorandAppId'],
['Sui', 'hex'],
['Aptos', 'hex'],
['Near', 'sha256'],
];
```
These entries define how the [`UniversalAddress`](https://github.com/wormhole-foundation/wormhole-sdk-ts/blob/007f61b27c650c1cf0fada2436f79940dfa4f211/core/definitions/src/universalAddress.ts#L23){target=\_blank} class handles different address formats based on the platform.
## Universal Address Methods
The `UniversalAddress` class is essential for working with Wormhole formatted addresses. It converts native blockchain addresses into the standardized 32-byte hex format used across Wormhole operations.
Key functions:
- **`new UniversalAddress()`**: Use the `UniversalAddress` constructor to convert native addresses into the Wormhole format.
```typescript
const universalAddress = new UniversalAddress('0x123...', 'hex');
```
- **`toUniversalAddress()`**: Converts a platform-specific address into the Wormhole formatted 32-byte hex address.
```typescript
const ethAddress: NativeAddress<'Evm'> = toNative('Ethereum', '0x0C9...');
const universalAddress = ethAddress.toUniversalAddress().toString();
```
- **`toNative()`**: Converts the Wormhole formatted address back to a native address for a specific blockchain platform.
```typescript
const nativeAddress = universalAddress.toNative('Evm');
```
- **`toString()`**: Returns the Wormhole formatted address as a hex string, which can be used in various SDK operations.
```typescript
console.log(universalAddress.toString());
```
These methods allow developers to convert between native addresses and the Wormhole format, ensuring cross-chain compatibility.
## Convert Between Native and Wormhole Formatted Addresses
The Wormhole SDK allows developers to easily convert between native addresses and Wormhole formatted addresses when building cross-chain applications.
### Convert a Native Address to a Wormhole Formatted Address
Example conversions for EVM and Solana:
=== "EVM"
```typescript
import { toNative } from '@wormhole-foundation/sdk-core';
const ethAddress: NativeAddress<'Evm'> = toNative(
'Ethereum',
'0x0C99567DC6f8f1864cafb580797b4B56944EEd28'
);
const universalAddress = ethAddress.toUniversalAddress().toString();
console.log('Universal Address (EVM):', universalAddress);
```
=== "Solana"
```typescript
import { toNative } from '@wormhole-foundation/sdk-core';
const solAddress: NativeAddress<'Solana'> = toNative(
'Solana',
'6zZHv9EiqQYcdg52ueADRY6NbCXa37VKPngEHaokZq5J'
);
const universalAddressSol = solAddress.toUniversalAddress().toString();
console.log('Universal Address (Solana):', universalAddressSol);
```
The result is a standardized address format that is ready for cross-chain operations.
### Convert Back to Native Addresses
Below is how you can convert a Wormhole formatted address back to an EVM or Solana native address:
```typescript
const nativeAddressEvm = universalAddress.toNative('Evm');
console.log('EVM Native Address:', nativeAddressEvm);
const nativeAddressSolana = universalAddress.toNative('Solana');
console.log('Solana Native Address:', nativeAddressSolana);
```
These conversions ensure that your cross-chain applications can seamlessly handle addresses across different ecosystems.
## Use Cases for Wormhole Formatted Addresses
### Cross-chain Token Transfers
Cross-chain token transfers require addresses to be converted into a standard format. For example, when transferring tokens from Ethereum to Solana, the Ethereum address is converted into a Wormhole formatted address to ensure compatibility. After the transfer, the Wormhole formatted address is converted back into the Solana native format.
### Smart Contract Interactions
In smart contract interactions, especially when building dApps that communicate across multiple chains, Wormhole formatted addresses provide a uniform way to reference addresses. This ensures that addresses from different blockchains can interact seamlessly, whether you're sending messages or making cross-chain contract calls.
### DApp Development
For cross-chain dApp development, Wormhole formatted addresses simplify handling user wallet addresses across various blockchains. This allows developers to manage addresses consistently, regardless of whether they work with EVM, Solana, or another supported platform.
### Relayers and Infrastructure
Finally, relayers and infrastructure components, such as Wormhole Guardians, rely on the standardized format to efficiently process and relay cross-chain messages. A uniform address format simplifies operations, ensuring smooth interoperability across multiple blockchains.
--- END CONTENT ---